Bartholin’s cyst removal is performed in our hospital as a day surgery procedure.
What is Bartholin’s cyst?
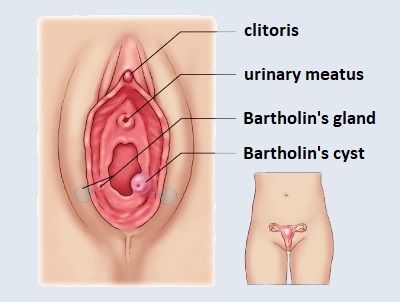
The Bartholin’s gland ensures the presence of vaginal mucosa. It is located in the lower third of the labia majora, at the vaginal entrance. There are two glands, about 1 cm, on each side, each with an outlet tube 2 cm long. Under normal conditions, Bartholin’s glands are not palpable, but the opening of their outlet tubes is mostly visible.
Inflammation of the glands is associated with pain, swelling, and sometimes fever. In addition to swelling, there is redness and throbbing pain, which can be felt more intensely when walking and sitting.
Bartholin’s gland inflammation occurs when pus-causing bacteria enter the gland’s outlet tube. The secretion that cannot be excreted is responsible for the formation of the so-called Bartholin’s cyst. If the gland is infected and the duct becomes blocked, it turns into an abscess.
What are the causes of cyst formation?
Bartholin’s cyst is mostly the result of a mixed infection caused by aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. It can also develop due to trauma or injury from episiotomy.
When is Bartholin’s cyst removal necessary?
Most women do not even know about the existence of Bartholin’s glands until they cause a problem (inflammation of Bartholin’s glands, painful cyst, abscess). The glands on both sides of the vaginal entrance are often at risk of infection.
If bacteria get into the outlet tube of the gland, it can become inflamed. In advanced condition, the whole gland becomes inflamed and can develop into an abscess.
Treatment of Bartholin’s cyst is necessary in case of pain and inflammation, it is done surgically.
How is the surgery performed?
The treatment of Bartholin’s cysts and abscesses is in all cases is surgical, it performed under anaesthesia.
The cyst is completely removed and then the wound is drained (to prevent the wound opening from closing) so that the secretion can be completely emptied.
In case of an abscess, the inflamed area is opened, the pus is removed, the abscess wall is scraped off, and then the cavity is rinsed with a disinfectant solution. In most cases, the wound is stitched with 2-2 stiches and then the wound is tamponed. The surgery takes approx. 10-15 minutes. The function of the tampon placed in the wound is to prevent the wound from closing early so that the secretion can be completely emptied.
What are the dangers of Bartholin’s cyst removal?
Bartholin’s cyst surgery is not dangerous, it has minimal risk. However, an untreated, mostly inflamed, painful cyst can lead to other health problems. It can be a source of fever, further infections and sexual problems.
