Hand surgery
Our hand is a tool for a significant part of our daily activities, work, hobby-sports activities, it is often a mediator of the expression of our feelings, when we touch our loved ones or in case of an artist. Due to its complex function and anatomy, a separate sub-discipline within medicine, hand surgery deals with hand injuries and their treatment.
What does a hand surgeon do?
The task of a hand surgeon is primarily to treat injuries and degenerative lesions of the hand, primarily surgically, and their aftercare, the main purpose of which is to restore and maintain sensory functions and restore fine movements.
In addition, the field of hand surgery also includes developmental disorders of the hand, inflammatory and cancerous lesions.
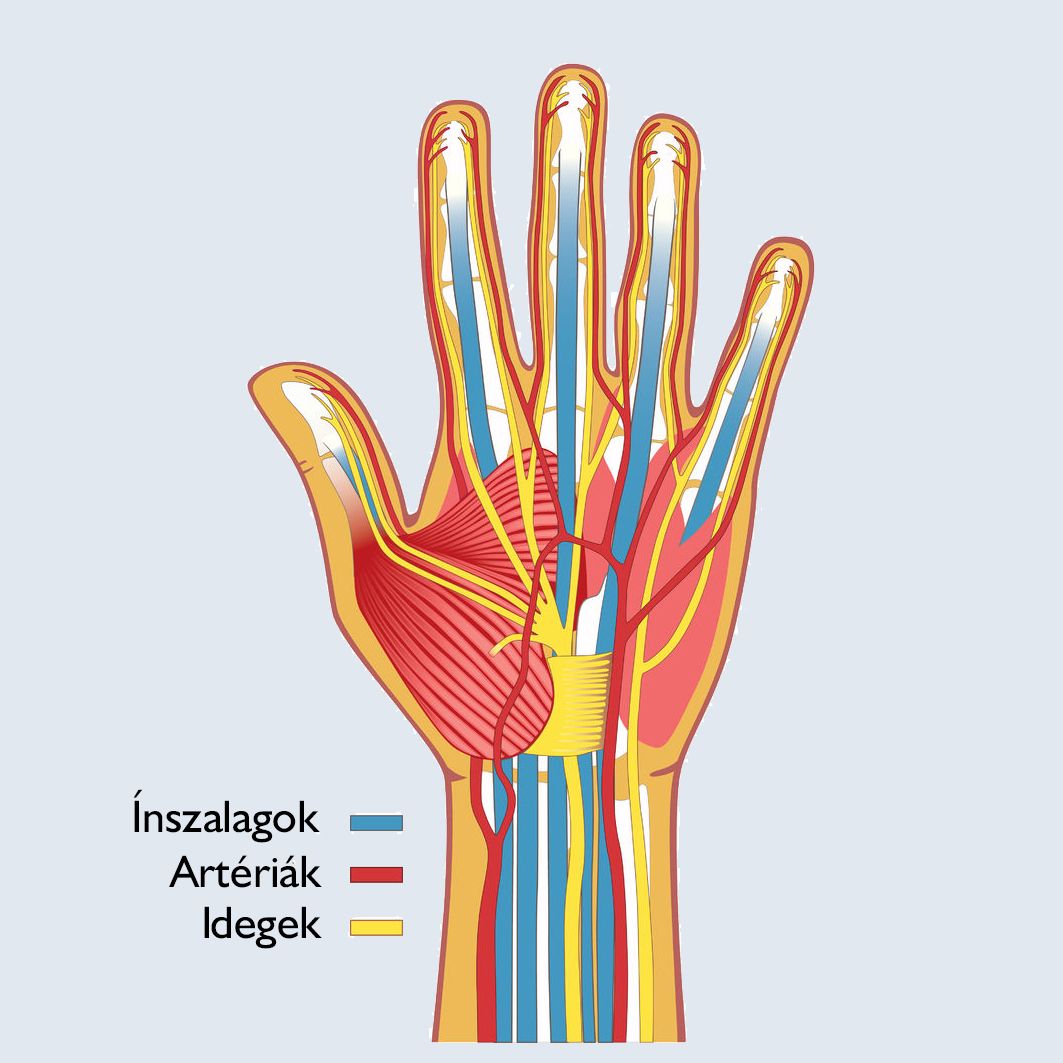
Restoring the structures of the hand requires special knowledge and extremely fine technique, as the coordinated operation of the hand is performed by complex tendon, nerve and vascular formulas, bone and joint systems, which requires the coordinated operation of nearly 200 fine formulas. To get to know them as accurately as possible, and to develop surgical technologies, hand surgery has become a separate field.
Successful treatment of hand lesions depends to a large extent on the training of the hand surgeon, supposes a thorough knowledge of the anatomy and functional anatomy of the hand, as well as a sound knowledge of the principles of hand surgery.
What types of injuries does hand surgery deal with?
Injuries of the hand are extremely common due to its many functions, accounting for ¼ injuries of the body. Most injuries are due to the grip function of the hand, but injuries during protective operation are similarly common (e.g., in the event of an accident when the hand is reflexively protecting the head or torso).
Hand injuries are often more severe than it would result from the injury alone. This is due to the fact that several formulas can be damaged at the same time, which in the case of improper care can cause coalescences around the tendons and the formation of scars, which can even cause subsequent loss of function. Therefore, in the case of hand injuries, the primary, professional care of the wound is to avoid the functional limitation caused by subsequent scarring.
Hand injuries can be varied, the most common types of injuries are summarized below. These injuries can also be treated by a traumatologist, but due to the complex anatomy of the hand, depending on the severity of the injury, seek the help of a hand surgeon if possible.
Minor hand injuries
Minor hand injuries include abrasions that only affect the upper layers of the skin and require sterile bandage and disinfection to treat them.
Injuries caused by a foreign body are also common, which can be caused by, for example, splinters and plant spikes. In such cases, the foreign body must be removed professionally as soon as possible.
In case of cut wounds, it is sufficient to unite the wound edges in case of smaller injuries that only affect the skin, but in the case of deeper injuries, it is important to treat the structures under the wound (blood vessels, tendons, nerves) to avoid later loss of function.
Bite injuries are also common and have an extremely high risk of infection, so the wound definitely requires professional medical attention. In the case of a hand bite, it is especially important that the care is performed by a hand specialist so that the injured formulas are united as accurately as possible.
Bruising of the hand can also be classified as a minor injury, but it should not be neglected in any way. In all cases, it is recommended to show the injury to a specialist to avoid subsequent tissue damage.
Skin injuries
In the case of skin lesions on the hands, it is important that the healing of the skin injury is accompanied by the least possible scarring. Depending on their size, skin lesions can be treated with sutures or skin replacement procedures.
Tendon injuries
Tendons are connective tissue-rich, resistant units responsible for the stability of joints, which transmit the strength of muscles to the bones. The extensor and flexor tendons on the hands and fingers provide all the movement needed for the hand to function smoothly. Their injury can be open and covered, caused by a sharp object, or by a spontaneous rupture that occurs when the fingers are suddenly abnormally strained. Injury of the tendon is usually easily recognizable, as some activity of the fingers of the hand is missing and deformity (curvature) is usually observed. Torn tendons can be repaired with sutures, but even after the repairing operation, the injured finger can be moved indefinitely.
Vascular injuries
Vascular damage can occur during open puncture, incision, bruising, or under compression. Closed injuries are most often direct injuries, e.g. they occur in connection with bone fractures and sprains. The injury is indirect if e.g. it is an overstretched rupture. Sometimes only one layer of the vessel wall is damaged, but this can already be a source of problem. If there is no palpable pulse, and if the limb is pale and cool, these can be symptoms of vascular injury of the hand. If vascular injury is suspected, care should be given as soon as possible because the risk of blood clots and other complications increases over time.
Electrical and thermic injuries
By thermic injuries, we mean burn and frostbite injuries. In case of burns, first aid, cooling with cold running water is very important. First-degree burns associated with erythema do not require special intervention other than analgesia and bandage. In case of second-degree burns with blisters, it may be necessary to open the blisters. In case of third-degree burns, it is always necessary to remove the damaged tissues.
In case of frostbite injury, warming up the limb is the primary task. When it comes to first-degree frostbite, swelling occur, in second-degree, necrosis of the surface tissues and blistering are observed. In the case of third-degree frostbite, the skin dies to its full thickness, damaging the deeper structures as well. In such cases, the removal of dead parts is necessary.
The electric current causes tissue damage in the epidermis, which often also damages the blood vessels running underneath. The current effect can cause temporary movement and sensory disturbances in the limb. It is advisable to excise dead areas as soon as possible to avoid later infections.

What hand surgery procedures are available at Medicover Hospital?
We perform the following hand surgery procedures in our hospital:
- Ganglion removal
- Benign tumour excision
- Trigger finger, tendon sheath incision
- Treatment of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
- Carpal tunnel syndrome surgery
- Treatment of Dupuytren’s contracture
- Hand skin deficiency plastic surgery
- Joint arthroplasty
- Elbow (cubital) tunnel syndrome
- Tennis elbow release
Convenience services
We accommodate our clients in a modern, pleasant, air-conditioned single room. Each room has a private bathroom, fridge and TV, as well as free WIFI access. We also provide our clients with individual nurse supervision, who will help your continuous recovery during your stay.

