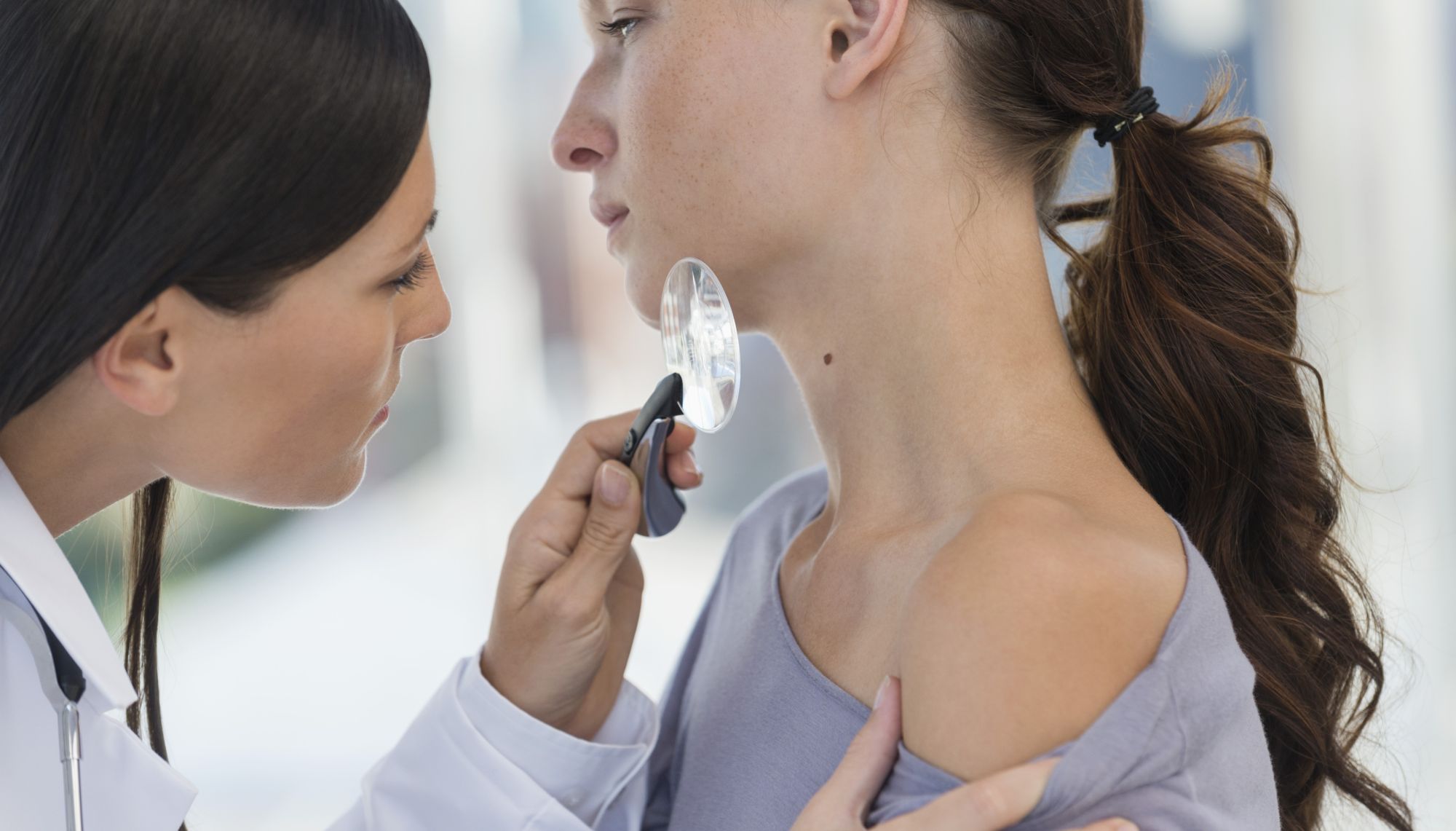
Dermatology
Dermatology is a discipline dealing with the aetiology and treatment of skin diseases, which also overlaps with allergology, virology, bacteriology and serology at several points due to the symptoms.
A dermatologist treats the lesions of the skin, hair, nails, oral mucosa, and external genitalia, as well as many sexually transmitted diseases.
With what symptoms should you see a dermatologist?
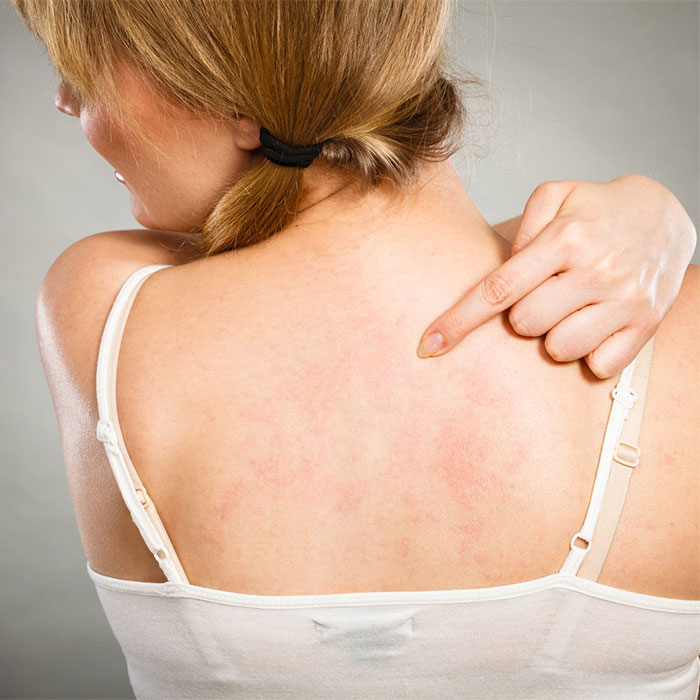
It is recommended that you see a dermatologist if you experience the following symptoms:
- the colour, shape, and size of the mole changes
- with pigmentation disorders (lack of pigments, liver spots, age spots, freckles)
- blisters and rashes of unknown origin appear on the surface of the skin or on the genitals
- allergic skin reaction, hives
- burning, itchy blisters and scars appear due to bacterial, viral or fungal infections
- after insect bites, blisters and rashes appear, the area around the bite is permanently inflamed
- in the presence of skin growths (e.g. fibroids in the folds of the body, neck)
- in case of permanent hair loss, baldness
- for effective treatment of dandruff scalp
- nail problems (nail fungus, ingrown nails)
- for the professional treatment of acne-prone skin
- herpes, scars
What diseases does the dermatologist treat?
Skin lesions can be noticed in time in most cases, therefore they can be successfully treated by consulting a dermatologist.
As part of a dermatology clinic and surgical care, we treat the following diseases in our clinics and in our hospital:
- Removal of premalignant (pre-tumour) lesions and melanoma: “moles” of altered colour, size, and shape should be seen by a dermatologist as soon as possible for timely removal.
- Removal of benign dermatological lesions: most often fibroids in the form of soft, brownish skin outgrowths, fatty tumours in the subcutaneous adipose tissue, i.e. lipoma, or atheroma due to swelling of the blocked sebaceous gland, get excised.
- Warts (verruca): a skin lesion caused by a viral infection that most commonly appears on the fingers and back of the hands, soles, torso, and around the genitals. The most common is the common wart (verruca vulgaris), which is easily recognizable by its cauliflower-like appearance, plantar warts (verruca plantaris), which can cause severe pain due to their location, swimming pool warts (mollusca contagiosa), which appear as glossy, dented hemispherical outgrowths, and sexually transmitted genital warts (verruca genitalis).
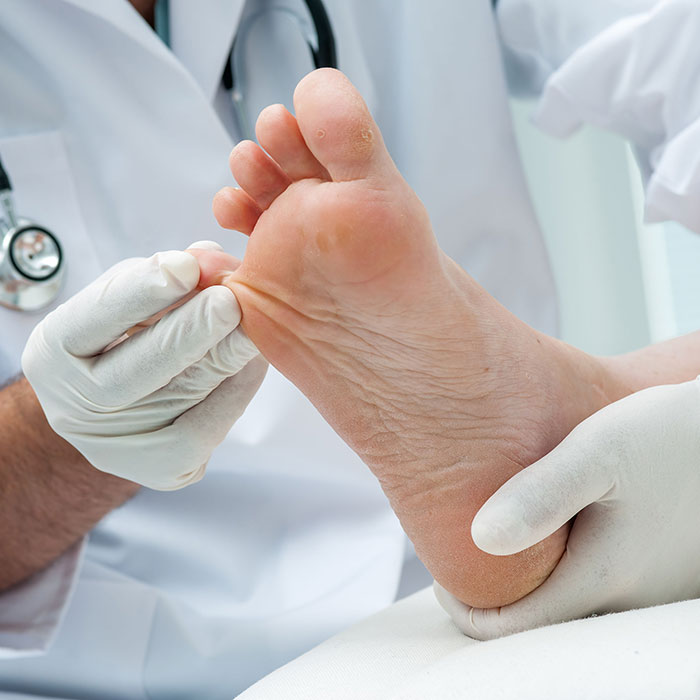
- Fungal infections of the skin, nails, and mucous membranes: is caused by fungal species of microscopic size that attack non-viable parts of the skin, the upper stratum corneum, hair, or nails. They cause a variety of symptoms, depending on where they occur: redness, painful blisters, protruding, scaly patches on the surface of the skin, and yellowed, thickened, crumbly nails.
- Dermatitis: an inflammatory reaction of the skin caused by an allergen. The skin usually becomes red, swollen, and itchy, sometimes scaly and can be wounded. Several types are known, atopic dermatitis due to genetic causes, contact dermatitis due to contact with an allergen, or seborrheic dermatitis caused by dead epithelial cells, so it is necessary to find out the cause in all cases for successful treatment.
- Acne-prone, pimpled skin: inflammation develops in the follicles that become blocked due to increased sebum production by the bacterium P. Acnes, which can lead to red spots, purulence, or even deeper, severe injuries with lumps and cysts, or scarring. It is easily treated with expert medical help.
- Rosacea: defective vegetative innervation of the blood vessels of the skin causes vasodilation on the face, a temporary redness that can persist for several days with small aneurysms on the surface of the skin. In its advanced state, acne-like rashes and larger lumps also develop because of the overgrowth of the sebaceous glands. With proper treatment, the deteriorating tendency can be slowed down and the already developed condition can be improved.
- Psoriasis: a non-communicable, immunologically induced skin disease occurs with red, protruding nodules with white, squamous scaly patches. In many cases, painful arthritis is also associated with skin symptoms. It can become asymptomatic with appropriate therapy.
- Shingles: following the virus causing chickenpox, a neuritis and dermatitis with red, swollen spots and blisters on the abdominal-chest area. Inflammation is also accompanied by scald-like pain due to nerve involvement, which can occur even before the blisters appear.
- Pigmentation disorders: a disorder in the formation of the skin’s pigment (melanin), which can cause increased or decreased function. In case of increased melanin production, liver spots, freckles, old spots occur, while in case of decreased production, vitiligo (light spots) or albinism can be observed.
- Sexually transmitted diseases: The diagnosis and treatment of diseases affecting the genitals, mostly sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhoea, syphilis, sexually transmitted herpes) are also diagnosed and treated by the dermatologist.
The course of a dermatological examination
The examination begins recording the patient’s medical history. The dermatologist will interview the patient in detail about their symptoms, previous illnesses, and previous disease that occurred in the family. The dermatologist will then examine the altered skin surface. If necessary, they take a closer look at the epidermis and the dermis with a magnifying glass or a special device with internal lighting and magnifying glass, called a dermatoscope.
If necessary, the dermatologist may order a blood test or refer you to another specialty, such as internal medicine, to rule out involvement of other organs, or to surgery to remove any skin lesions.