Minor ophthalmic surgeries
Our ophthalmic procedures include excision of barley, atheroma, fibroids and all kinds of lesions, pterygium removal, bilateral upper eyelid surgery, treatment of lower eyelid inversion and ectropion.
With which complaints should we contact an ophthalmologist?
If your vision deteriorates, you experience blurred vision, eyeball pain, your eyes become inflamed or red, you notice swelling around your eyes, your eyes get watery, become particularly sensitive to light, it is definitely recommended to see an ophthalmologist.
The following ophthalmic surgeries are performed under local anaesthesia at our hospital.
Barley removal
Barley is an inflammation of the glands around the eyes. Inflammation of the glands on the inner surface of the eyelid is the inner barley (Hordeolum internum) and inflammation of the glands on the outer surface of the eyelid is the so-called outer barley (Hordeolum externum). Outer barley usually appears as a red, painful swelling at the edge of the eyelid. Inner barley, on the other hand, does not necessarily cause a visible lump.
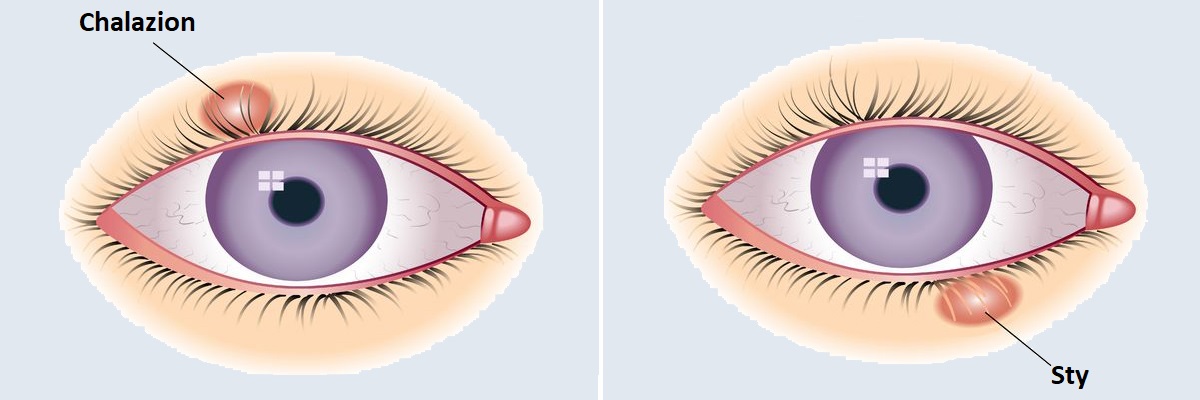
Weakened immune systems (susceptibility to infections), wind, dusty air, or a polluted environment, as well as bad habits such as regular rubbing of the eyes, can play a significant role in the development of barley. If it does not heal with medication, a surgical opening is performed. Barley removal is a small ophthalmic operation that takes place on the inside of the eyelid, from the conjunctiva. Purulent sebum excretion, which cannot be emptied, is removed and, in most cases, the inflammatory granulation tissue is also excised. At the end of barley removal surgery, there is no need to suture the wound. After the procedure, a pressure bandage is placed on the eye.
Atheroma removal
An atheroma, or sebaceous gland, is a benign lesion located just under the skin. It is caused by a blockage in the outlet tube of the sebaceous glands. Not only can it cause an aesthetic problem, but it can also become infected, resulting in the formation of abscesses and then persistent discharge. It is removed as part of a minor ophthalmic surgery. During surgery, the pulpy lump is completely removed through a wound. The wound is then closed with a plastic suture. Finally, a dressing is placed on the wound, supplemented with a haemostatic pressure dressing if necessary.
Cyst removal
The eye cyst is a benign, water-filled lump with a thin sheath that can occur on the conjunctiva. The reason for its formation is the occlusion of the outlet tube of the lacrimal gland. Lacrimal glands help keep the eye moist. An eye that does not regularly get the right amount of tears can become very painful. The cyst also has a wall and a cavity, so it is removed along with the sheath to prevent recurrence.
Fibroma removal
Fibroma is a benign tissue proliferation of connective tissue cells that develops in most cases in middle-aged people, primarily in women. It is more common in overweight people. It does not cause health problems but it can be easily irritated or aesthetically annoying due to its location. It is removed by surgical excision.
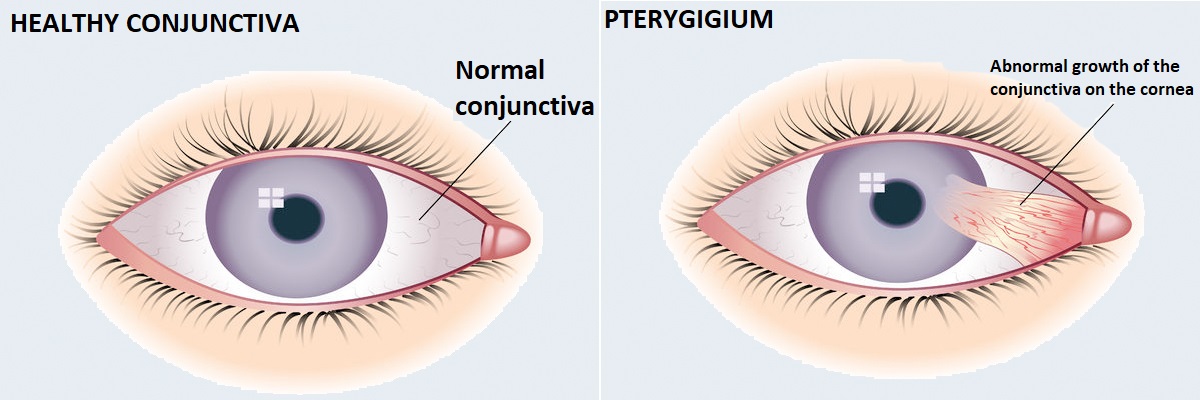
Pterygium
The pterygium is the conjunctiva that extends to the cornea. It occurs most often in the nasal region and is usually bilateral. It consists of head, body and neck. It is not uncommon for the lesion itself and its surroundings to become increasingly vascular and red. At that point, it only causes an aesthetic complaint. In advanced cases, it also reaches the centre of the cornea, causing visual impairment. It is removed surgically. During the procedure performed within the framework of minor ophthalmic surgeries, the abnormal conjunctiva is detached from the cornea.
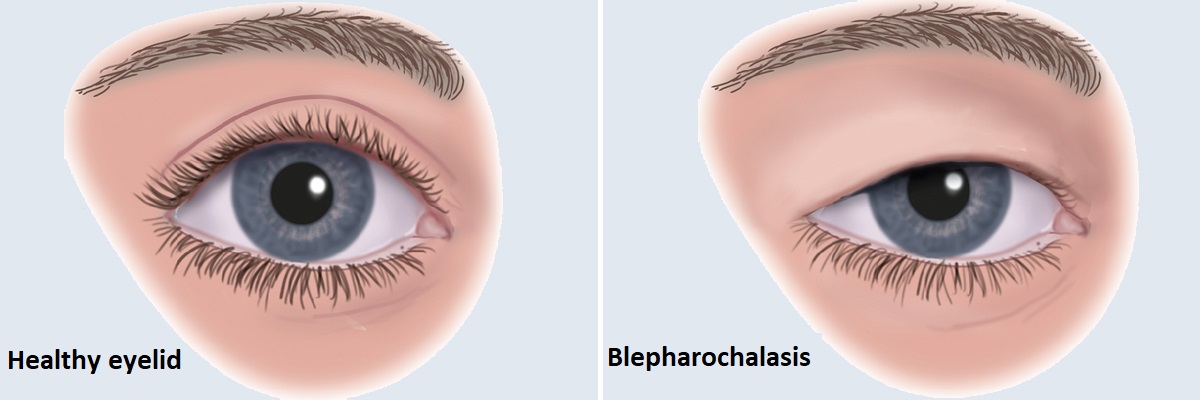
Looseness of the skin of the upper eyelid (blepharochalasis)
Hanging of the skin of the upper eyelid to an extent that has little or no effect on the opening of the eyelid. It usually occurs on both sides. It does not affect vision. The surgical procedure is for aesthetic purposes. Generally, surgery is recommended when the skin rests on the lash line.
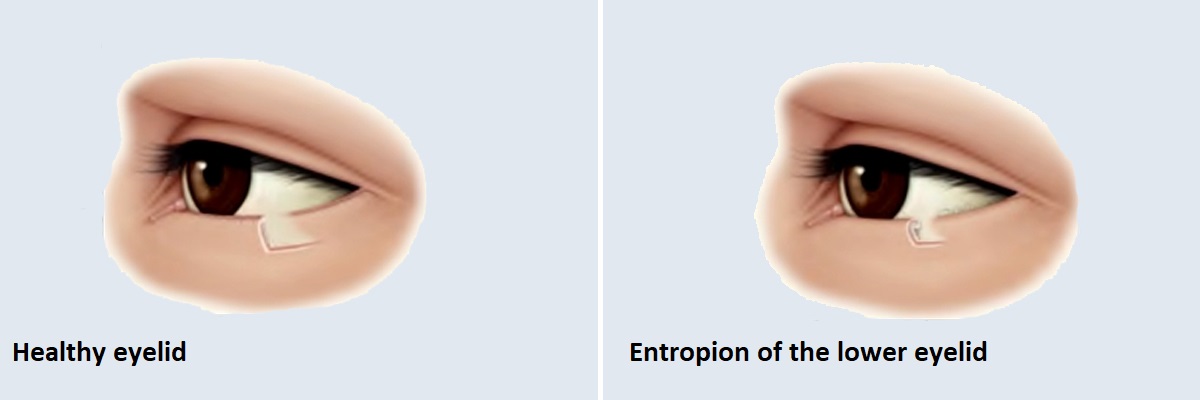
Treatment of entropion of the lower eyelid
Inversion of the entire lower eyelid, causing the lash line to come in contact with the eye surface. Because of irritable complaints that do not want to go away, and in many cases, the diminution of the cornea lead to a serious eyelid disorder. It can appear on one or both sides. Restoration of eyelid inversion is always surgical, which, in addition to the aesthetic purpose, means preserving or regenerating the condition of the eyeball. The cause of abnormal eyelids is an overgrowth of the locomotor muscles, and thus overactivity. During surgery, a wound parallel to the edge of the eyelid is incised on the skin of the lower eyelid and the abnormal, enlarged muscle is removed.
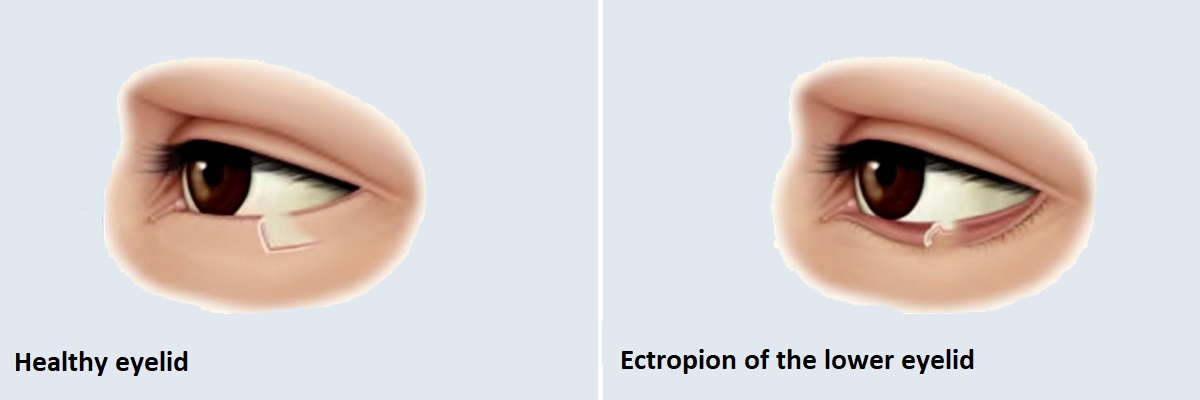
Lower eyelid ectropion
Unilateral or bilateral twisting of the lower eyelid. It most often occurs as a result of connective tissue relaxation associated with age. It is caused by weakening of the tendon plate of the eyelid. As a result of the abnormal eyelid, the conjunctiva of the eye is in constant danger in contact with the outside world, therefore the elimination of the disease is also recommended for the protection of the eye in addition to the aesthetic purpose. Restoration of the eyelid disorder is always done surgically.
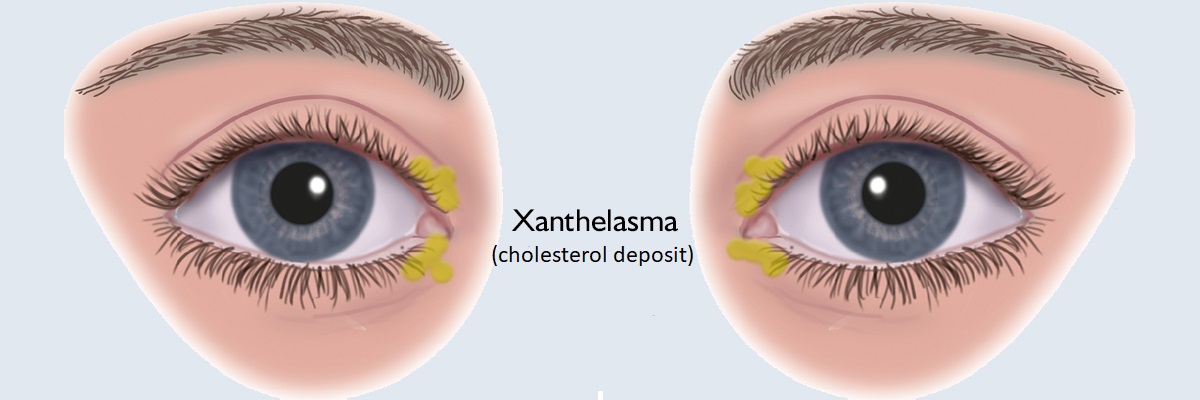
Xanthelasma
Xanthelasma is a yellowish, slightly prominent, velvety-touch cholesterol deposit on the upper and lower eyelids, and it is symmetrical in most cases. It is removed by excision.
Am I fit for surgery?
Minor ophthalmic surgeries should be considered in the following cases:
- diseases affecting the immune system make healing difficult
- if there are several eye diseases at the same time, cataract surgery may not be possible

