Arthroscopic knee surgery, knee arthroscopy, knee surgery
Knee arthroscopy is one of the most commonly used procedures in the diagnosis and treatment of knee injuries. This minor surgery is performed using a small device about the size of a pencil, called an arthroscope.
Arthroscopy is performed through small incisions. During the procedure, a knee specialist orthopaedic surgeon inserts the arthroscope into the knee joint and uses it to find, repair, or remove damaged parts.
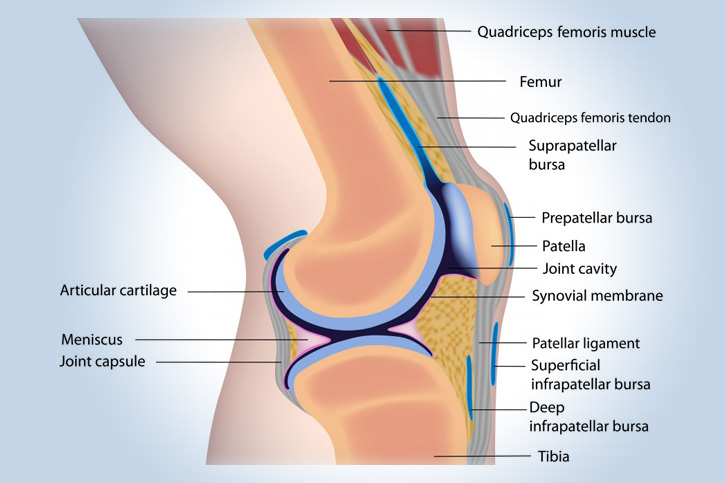
What are the parts of the knee?
The knee is the largest and one of the most important joints in the body. It is a strong but flexible wrist joint that plays a fundamental role in movement when carrying body weight in the horizontal (running and walking) and vertical (jumping) directions.
Between the femur and the tibia is the meniscus (a crescent-shaped cartilage located in the knee joint), a layer of hard fibrous cartilage that acts as a hit reducer.
The knee joint is exposed to injuries that most commonly occur during sports or leisure activities, work tasks, or housework.
What are the most common knee diseases?
Patellar dislocation
The patella fits into a hole in the femur in front of the knee. In a painful knee, the patella may lean to the outside of the knee.
This occurs when the thigh muscles exert a chronic outward pulling force on the kneecap, which puts a strain on the internal tissues (the retinaculum). In case of arthroscopic sheath incision of the kneecap or in case of a serious disorder, tuberositas tibiae medialization is performed.
Loose body in the knee
Loose body is another name for a small piece of debris floating freely in a joint. As a result of cartilage detachment, it often happens that the detached piece (loose body or “joint mouse”) migrates by swimming in the synovial fluid. If it floats between cartilage surfaces, it causes joint closure.
As a result, knee movement will be restricted (will not be able to bend or strech). A loose body usually causes severe pain and is often palpable. In this case, an arthroscopic loose body removal is performed so that the trapped piece does not cause permanent cartilage damage or cartilage wear.
Meniscus tear
Injury to the meniscus means rupture, which in more severe cases can lead to cartilage detachment. In such cases, it is recommended that the detached piece be removed as soon as possible to avoid damage to the hyaline cartilage at the end of the joints.
Injury to the medial meniscus is more common because it is more attached to the joint capsule, so it can dodge less and be more easily pinched between the articular surfaces.
Orthopaedic surgeons most often perform meniscus resection.
Anterior cruciate ligament tear
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) helps stabilize and support the joint. Injury to the anterior cruciate ligament is common, especially in case of athletes. The ACL can be damaged if the knee joint is bent backwards or moved quickly laterally, or if the above occurs simultaneously. The most common surgical procedure in this case is arthroscopic ACL reconstruction.
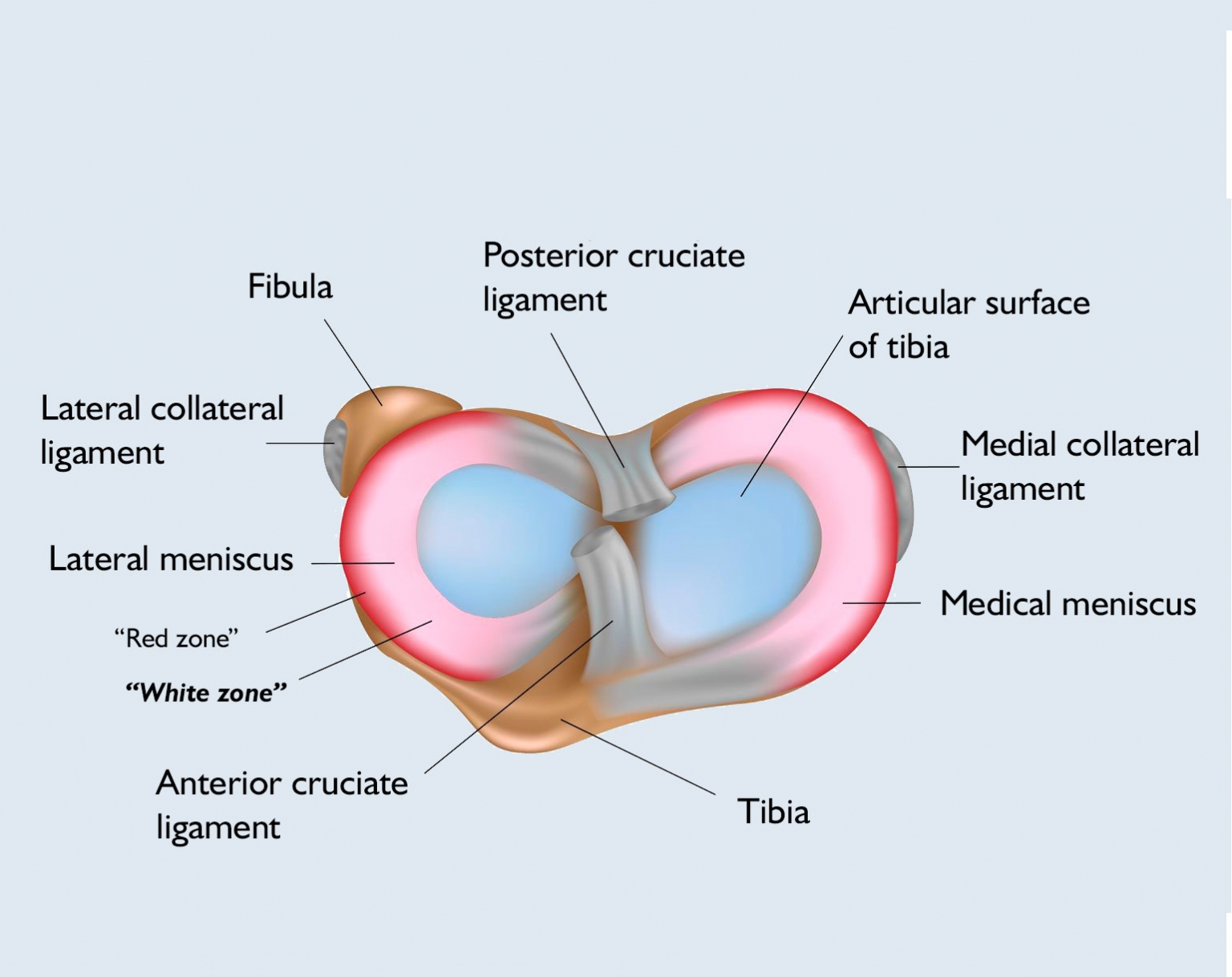
Chondropathy (softening of cartilage)
There may even be an osteochondral lesion, which is an injury to the smooth surface at the end of the bones, such as wear on the articular cartilage and tibia or femur bone in the knee joint. Arthroscopic knee cartilage shaving and in severe cases arthroscopic shaving mosaicplasty can be used to treat these diseases with surgical procedures.
Mosaicplasty, a form of chondral grafting, is a surgery to replace cartilage on the surface of the knee joint damaged by trauma or arthritis, by implanting osteochondral plugs. Depending on the severity and overall size of the injury, more plugs may be needed to properly treat the joint.
What surgical procedures do we perform?
Meniscus surgery (removal of damaged parts of cricoid, fibrous cartilage)
Meniscus tear is treated surgically by re-fixing or removing the ruptured part by a knee specialist orthopaedic surgeon. In our hospital, meniscus injuries are treated with an arthroscopic procedure.
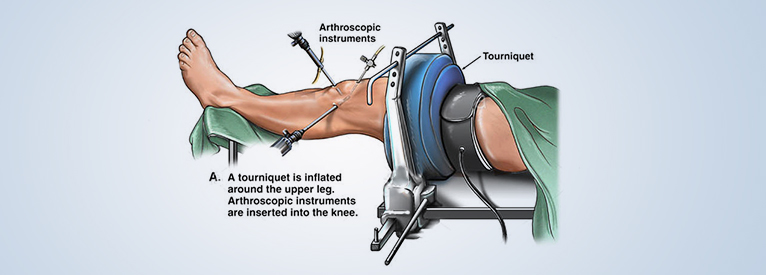
This precise, minimally invasive technique allows much faster healing, as injured cartilage can be healed with minimal tissue damage, without open exploration.
Arthroscopic mosaicplasty
Mosaicplasty is a technique in which small (4-8 mm) circular autogenic grafts are lifted out of the non-load-bearing regions of the knee and the grafts are implanted in a mosaic-like manner to replace a cartilage deficiency (osteochondral defect).
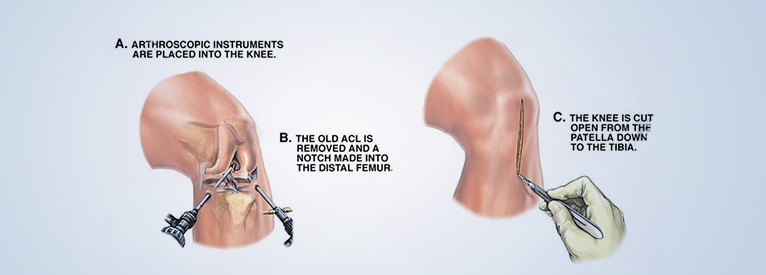
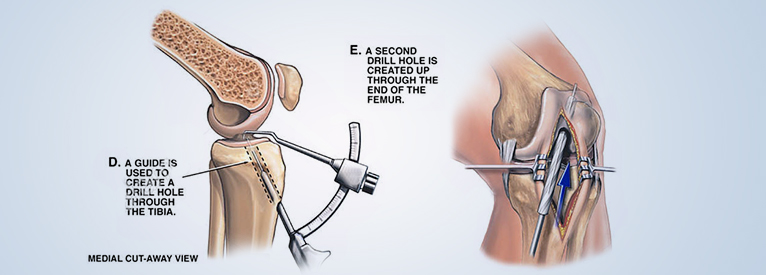
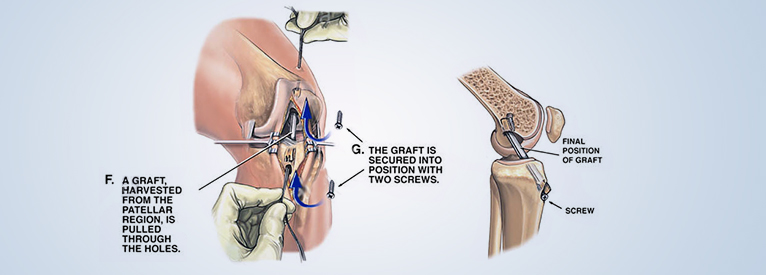
Arthroscopic ACL reconstruction
Arthroscopic ACL surgery is performed only after the immediate swelling and inflammation after injury has eased.
When the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) is completely torn, the surgeon must replace it with a graft, which is usually obtained from the patient’s own knee (called an autograft).
The biggest advantage of surgery is that it requires minimal hospital stay and rehabilitation is accelerated due to anatomical reconstruction, it only takes a few weeks to recover.
Arthroscopic joint loose body removal
Nowadays, the procedure to be followed is to remove all loose bodies by arthroscopy, more commonly known as “cleansing” arthroscopy. This minimally invasive procedure allows the surgeon to thoroughly examine the loose bodies in the knee and allows cartilage injuries to be assessed and the disease to be treated.
Arthroscopic knee cartilage shaver procedure
This general treatment is used in case of patients whose cartilage defect has not worn down to the bone. The surgeon inserts a pencil-thin arthroscope into the knee through a small incision, shavers and smooths the fragmented or worn cartilage. Ideally, smoothing and using shavers on the damaged cartilage will help reduce friction and irritation, thus reducing the symptoms of swelling, murmur and pain.
Arthroscopic lateral release of the patella
In the process, an incision is made in the lateral stabilizing structure of the patella, in particular in the lateral retinaculum. The lateral reticulum connects the lateral kneecap to the external protrusion of the femur, the iliotibial ligament, and the anterior-lateral part of the tibia. Arthroscopic lateral release is usually performed in combination with medial-based stabilization procedures, allowing more efficient medial adjustment.
What are the advantages and risks of surgery?
Knee arthroscopy is a safe procedure for treating knee injuries and is minimally invasive. The advantage of arthroscopy over traditional open surgery is that there is no need to fully open the joint. Only two, sometimes three small incisions are made – one for the arthroscope and one for the surgical instruments to be used in the knee cavity.
This reduces healing time and can increase the success rate of surgery due to less trauma to the connective tissues. In case of most people, the procedure only takes an hour or two. The scarring is also smaller due to smaller incisions.
Arthroscopic knee surgery is an effective tool in diagnosing joint diseases and strengthening the treatment of knee problems such as meniscus tear and cartilage wear.
Arthroscopy can ultimately relieve knee pain and improve mobility. One of the most important benefits of the procedure is the maintenance of a normal and active lifestyle.
In the case of arthroscopic knee surgery, possible postoperative problems are rare and easy to treat. The following might occur: infection inside the joint, blood clot, deep vein thrombosis/embolism, knee stiffness, injury or damage to cartilage, ligaments, meniscus, blood vessels or nerves.
Am I fit for knee surgery?
The number of knee surgeries has almost doubled in less than 10 years. If you experience pain in your knee, it is recommended that you consult a surgeon to spare your knee joint and delay or possibly prevent the onset of more serious knee problems.
The surgeon will suggest the best procedure because several factors need to be considered before someone decides on knee surgery, let alone the different types.
How do I prepare for surgery?
If you choose arthroscopic knee surgery, a full physical examination is needed before the surgery to assess your health and identify factors that may be interfering with the surgery.
Before surgery, tell your orthopaedic surgeon if you are taking any medications or supplements. Your doctor will tell you which medications you should stop taking before surgery.
When staying in the hospital, be sure to bring everything you will need during this time.
What should I do after knee surgery?
Recovery from knee arthroscopy is much faster than from conventional open knee surgery, yet it is important that you carefully follow the instructions of the knee specialist orthopaedic surgeon after returning home. Some algesia is a natural part of the healing process.
After surgery, we often prescribe medications to quickly relieve pain. To relieve swelling and pain, your surgeon may recommend chilling. It is important to keep the incision site clean and dry.
The surgeon will tell you when and how to take a shower or bath. Most patients need crutches or other assistance after arthroscopic surgery. The surgeon will tell you when you can safely strain your legs.
Why are regular follow-up examinations after surgery important?
Physiotherapy plays an important role in early recovery. For a few weeks, you should exercise regularly your knees after surgery to restore movement and strengthen important muscles.
Recommended postoperative follow-up examination in case of ACL
Once you get home, put ice on your knees for 15-20 minutes per hour for the next few days, but keep the bandage dry. Ice helps reduce pain and swelling. In the first 1-2 weeks after surgery, the most important goal is to be able to fully straighten your knees again.
This is much more important at first than being able to cover long distances on foot. Too much walking will cause your knee to swell and hurt, preventing you from stretching your knee. Leave the dressing up until the first postoperative follow-up examination.
Recommended postoperative follow-up examination in case of arthroscopic knee surgery
Immediately after surgery, if pain while walking is minimal, it is not necessary to use a crutch or walker. If needed due to pain, the patient may choose to use a crutch or walker for a few days after surgery.
Most patients experience the benefits of arthroscopic knee surgery within 4-6 weeks. The reduction in pain and swelling, as well as the improvement in knee strength, movement, and coordination, can last for 3-4 months after surgery. A follow-up appointment should be scheduled for 6 weeks after surgery.
