Pulmonology
The pulmonologist deals with diseases of the lungs and the respiratory tract. Lung diseases usually do not occur alone, but often with diseases of other organs.
Today, more than 600,000 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and more than 250,000 patients with bronchial asthma live in Hungary.
Our pulmonologists have extensive experience in the investigation and care of respiratory allergic diseases.

With what symptoms is it worth visiting a pulmonology clinic?
- shortness of breath
- chest pain
- night sweats, suffocation
- increased secretion
- cough (productive or unproductive)
Lung disease may be indicated by inflammatory factors in the blood count (Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, high white blood cell count, high CRP).
Pulmonology also treats the respiratory symptoms associated with reflux and diagnoses respiratory failures (e.g. sleep apnoea).
Systemic fungal infections affecting the lungs, viral bronchitis, and bronchiectasis (irreversible dilatation of the bronchi) should be mentioned as well.
What diseases does pulmonology deal with?
- asthma
- allergy
- pulmonary fibrosis
- pneumonia
- adenocarcinoma
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
In case of large cell lung cancer, lung tumour or pulmonary embolism, it is necessary to visit a lung center or emergency care.

The course of the general pulmonary examination
Having questioned the patient and recorded the medical history, the pulmonologist, if deemed necessary, helps diagnose the problem with imaging procedures (CT, MRI, ultrasound and X-ray, which are carried out as part of a separate diagnostic examination, at a separate appointment and for a fee).
For the examination of allergic symptoms, the pulmonologist orders a laboratory blood test or skin test (Prick test), which is performed by a dermatologist.
When it comes to private pulmonary practices, a common diagnostic procedure is the respiratory function test, spirometry, during which patients breathe in and out through a bell-shaped device. The pulmonary examination is suitable for examining the condition of the lung tissue, it shows whether the patient has lung damage or not.
During the examination, the presence of Asthma and COPD is examined, and a proposal for prevention is made.
What treatment options are available for the diagnosed problems?
Based on the examination, during the private pulmonary practice, the specialist adjusts the medication, prescribes the frequency of control or the need of hospital care, surgery.
In case of asthma, it can be reduced or eliminated with medication, but in a given case, the symptoms of the disease can be prevented (with the help of preventative or maintaining, and attack-relieving agents).
When it comes to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), the ultimate goal is to alleviate complaints, improve quality of life, and to stop, slow down the deterioration of lung function with medications and non-drug therapies.
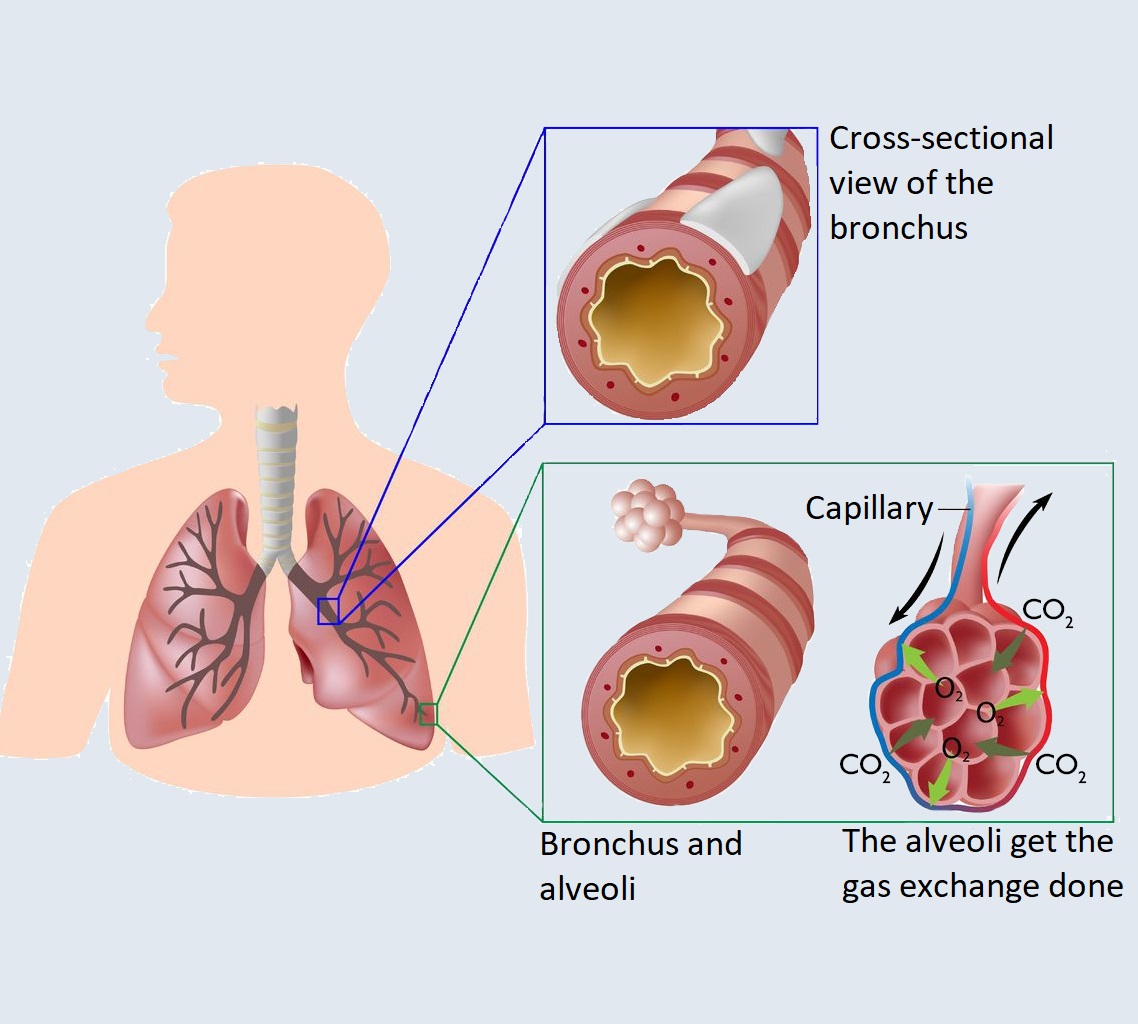
Anatomy of the lungs
The lungs are part of the respiratory system, although their weight is small, but they fill a large part of the chest cavity. When extended, the surface of the lungs corresponds to the size of a tennis court – approximately 100 square meters.
The lungs are a spongy, paired organ made up of lobes. The two lungs are not the same size because part of the chest is occupied by the heart, so the left lung is smaller. The lungs provide our bodies with oxygen. They do not have their own muscles, their movement is initiated by the functioning of the chest and the diaphragm.
When inhaling, air passes through the mouth or the nasal cavity, through the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and larynx.
It continues its way through the trachea, then through the bronchi (meanwhile the inhaled air is cleansed, heated up and its humidity is increased), and then through the bronchial system, then reaches the alveoli where the gas exchange is taking place.
