Laboratory tests for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) for women and men (blood sample)
This package includes tests for sexually transmitted infections (syphilis, HIV, HCV, HSV herpes simplex I-II), which detect the antibodies of infectious pathogens from the blood.
The appearance of antibodies in the blood varies, they will be detected weeks later in the case of HIV and hepatitis C infections, so it is recommended that the test be performed 3 to 4 weeks after the presumed time of infection if these diseases are suspected.
Sexually transmitted diseases are characterized by asymptomatic incubation in the body for many years or minimal, uncharacteristic symptoms. In many cases, the test happens only when the processes are already in an advanced, irreversible state and complications appear. Neglected infections also increase the chances of infertility, the development of complications during pregnancy (miscarriage, premature birth), and the infection of the newborn.
Which items are included in the STD laboratory test?
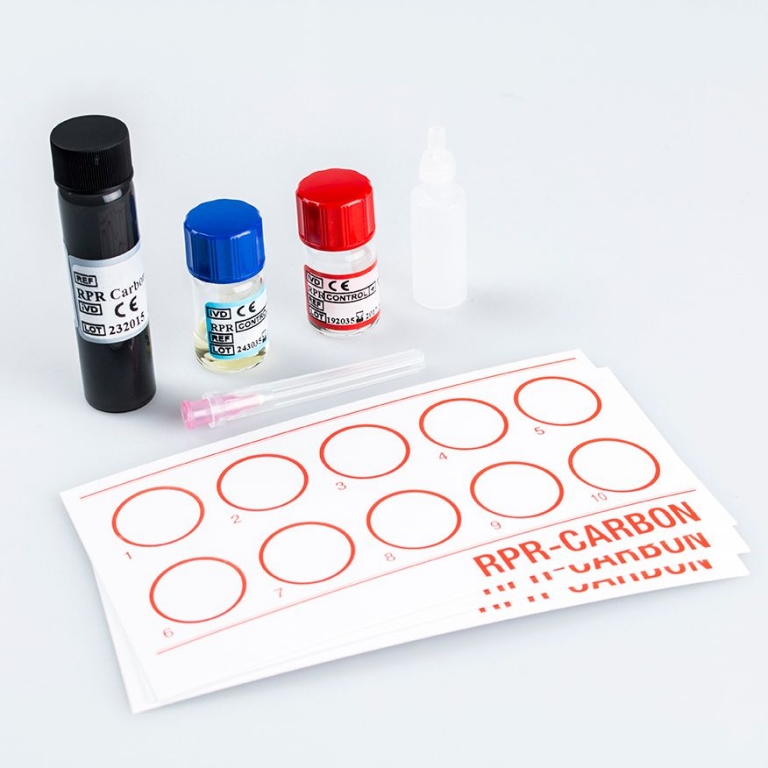
Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR)
The test is the causative agent of a sexually transmitted disease called Treponema pallidum, syphilis. Syphilis (lues or French disease) is transmitted through sexual contact but can also be transmitted directly by blood.
It does not prevent childbirth, but in case of an infected mother, the child is also born infected due to contact with the birth canal. Without treatment, the disease occurs at different stages, each of which is characterised by skin symptoms.
The RPR (Rapid Plasma Reagin) assay detects IgG and IgM antibodies produced against lipoid released from damaged cells, and lipoid-like substance released from spirochaetes. These antibodies are present 4-6 weeks after infection, and then disappear from the serum after successful treatment of the infection.
This procedure is perhaps most important in detecting the HIV virus, i.e. proving AIDS seropositivity.
HIV
The virus that causes AIDS destroys the body’s defence system: it infects immune cells, blocks their function, making the human body vulnerable to infections.
Thus, up to 10 billion viruses can be formed in an infected body every day, causing immune cell death until the immune system is completely weakened. The disease is spread primarily through sexual transmission through infected genital secretions but can also be transmitted by infected blood. The latter happens with the joint use of needles and syringes by drug users.
HCV
The pathogen enters the bloodstream through tiny, even invisible mucosal lesions. Dangerous means are shared devices that are not kept clean and cause minor injuries (acupuncture and tattoo equipment, manicure sets, razors, toothbrushes), and people often changing their sexual partners are at increased risk.
It causes infectious hepatitis, but its symptoms also include high fever and jaundice. The target cells of HCV are primarily liver cells, but the virus also infects other cells in the body, e.g. white blood cells.
HSV Herpes simplex I-II
In the initial stage, it is usually asymptomatic. After the first infection, the incubation period is at least 20 days. Later, however, painful, blistering, wound herpes similar to mouth herpes appears around the genitals of those affected. It is not uncommon to experience fever and lymph node enlargement. It can be transmitted through sexual intercourse, and passed from mother to child during birth.
How do I prepare for the test?
Laboratory tests for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) for women and men do not require an empty stomach.
When is the result expected?
7 working days and in case of a positive result 14 working days.
