Extended blood and urine test
Our extended blood and urine test contains general laboratory screening tests. With the help of this test lots of diseases could be detected at an early stage, before you experience any complaints. The tests included in the package give an overview of the body’s function: carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, the liver, kidney function, the condition of the hematopoietic system, the function of the thyroid gland and inflammation in the body.
When is it recommended to perform an extended blood and urine test?
For general complaints such as frequent headaches, weakness, general malaise, pallor, fatigue, an extended blood and urine test is recommended, which may help the physician determine the cause of the complaint.
It is recommended that an extended blood and urine test is carried out once a year, on a screening basis, especially in the event of increased physical and / or mental strain.
Our health package, compiled individually for women and men under the age of 50 and over 50, which includes specific laboratory tests according to the needs of the given age group, provides a more comprehensive picture of the general state of health than an extended blood and urine test.
What tests does the extended blood and urine test include?
Function of the hematopoietic system
Blood count: is used to determine the relative and absolute numbers of shaped elements in the blood, red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (fvs), and platelets (THRs). From this, the specialist may conclude, among other things, anemia, blood loss, inflammatory processes, disease of the hematopoietic organs and coagulation disorders.
Liver function
Bilirubin is produced as a yellow breakdown of red blood cells in the spleen, liver and certain lymph nodes. Its levels may rise in cases of increased red blood cell breakdown, liver disease and biliary obstruction.
GOT (glutamate oxaloacetate aminotransferase) is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of amino acids. It is normally present in small amounts in the blood, but increases in the case of organ damage. A lower GOT value can be found in pregnant women.
GPT (glutamate pyruvate aminotransferase) is an enzyme produced in liver cells that shows the damage that has taken place there. Normally, it is also present in small amounts in the blood, increasing in case of damage.
GGT (gamma-glutamyltransferase) is an enzyme produced by the liver, pancreas and kidneys. It is an important indicator of the health of the liver and the bile ducts.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): an enzyme that helps break down proteins. It usually provides information for liver and bone disease testing. A high value indicates liver or bone disease (eg, osteoporosis), a lower value may be due to hypothyroidism, malnutrition, or anemia.
Fat and carbohydrate metabolism
Blood sugar laboratory test is used to determine the level of glucose in the blood to help identify diabetes. Elevated levels indicate you suffer from the disease.
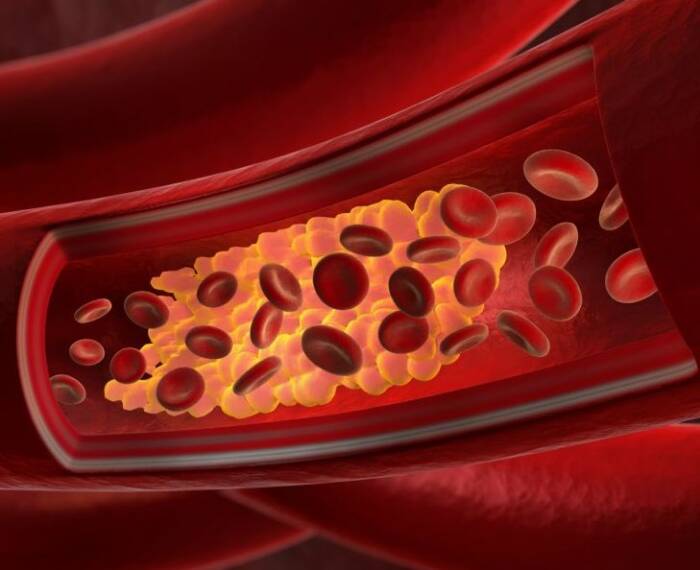
Cholesterol is produced in the highest amount by the liver, but some of it is taken in with food. The cholesterol produced by the liver is essential for the production of bile. Total cholesterol is determined in a laboratory test and the proportions of LDL and HDL cholesterol are also indicated.
HDL cholesterol is the “protective” cholesterol. It transports cholesterol deposited in the vessel wall back to the liver, preventing atherosclerosis.
LDL cholesterol is “bad” cholesterol. It transports cholesterol from the liver to the cells, which can deposit in the blood vessel walls, reducing their elasticity and increasing the risk of atherosclerosis and heart attack.
Triglyceride is a component of fats ingested during diet, that supply energy to the body. Ideally, it occurs in small amounts in the body, but in case of excessive carbohydrate intake, our body also produces triglycerides.
Inflammation
CRP test measures the amount of CRP protein that is produced in liver cells in case inflammation occurs. Typically, its levels increase radically in bacterial and fungal infections. A laboratory test can only detect inflammation present in the body, but not its exact location. In the presence of inflammation, further testing is recommended.
Kidney function
Urine with sediment: This test is used to detect infection, metabolic abnormalities, and renal disease.
Urea: a breakdown product of amino acids, also an indicator of kidney function. Elevated levels usually indicate kidney failure.
Creatinine (with eGFR): a degradation product derived from muscles, the level of which is relatively constant in the human body. It is excreted through the kidneys, so its elevated levels in the blood indicate kidney disorders.
Thyroid function
TSH: We study the levels of the thyroid-stimulating hormone, which is produced in the pituitary gland and stimulates thyroid hormone production. If the TSH is elevated, the thyroid gland is underfunctioning, if the TSH value is lower, increased thyroid function may be the cause.
How to prepare for the examination?
Please arrive on an empty stomach for the blood sampling. A sample submitted in a clean container is required for urine testing.
How long does it take to receive your results?
On the second working day after sampling.
