Hip prosthesis surgery
If your doctor has recommended a hip prosthesis, this summary will help you with all the information including the necessary preparation, the complete procedure and the post-operative things to do.
Prosthetics is the most successful intervention in modern medicine today. Hip prosthesis surgery allows the movement of the patient’s hip joint to be complete or painless again after the procedure.
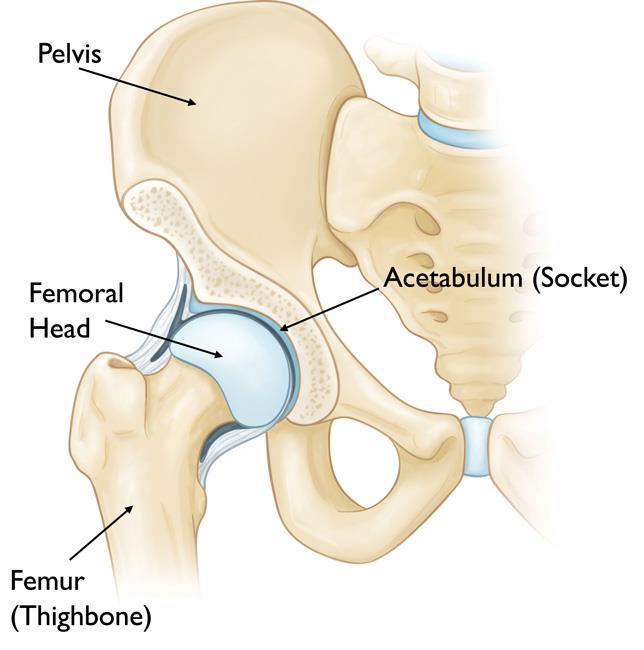
Structure of the hip joint
The hip joint is located between the head of the upper tibia and the pelvic joint.
The head of the femur, covered with spherical cartilage, is received by the articular cavity in the pelvis. The joint is held in place by the joint sheath and ligaments and is moved by the muscles that stick to the two bones that make up the joint.
When is hip replacement surgery necessary?
Hip replacement surgery may be warranted in the following cases:
- In case of severe cartilage wear of the hip joint, called arthrosis (wear of the joint and the cartilage surfaces)
- In case of fracture of the femoral neck or head
- In case of femoral head necrosis after femoral neck fracture
- In the event of an accident with a major force involving the parts of the articular cavity or the femoral head.
How is hip replacement surgery performed?
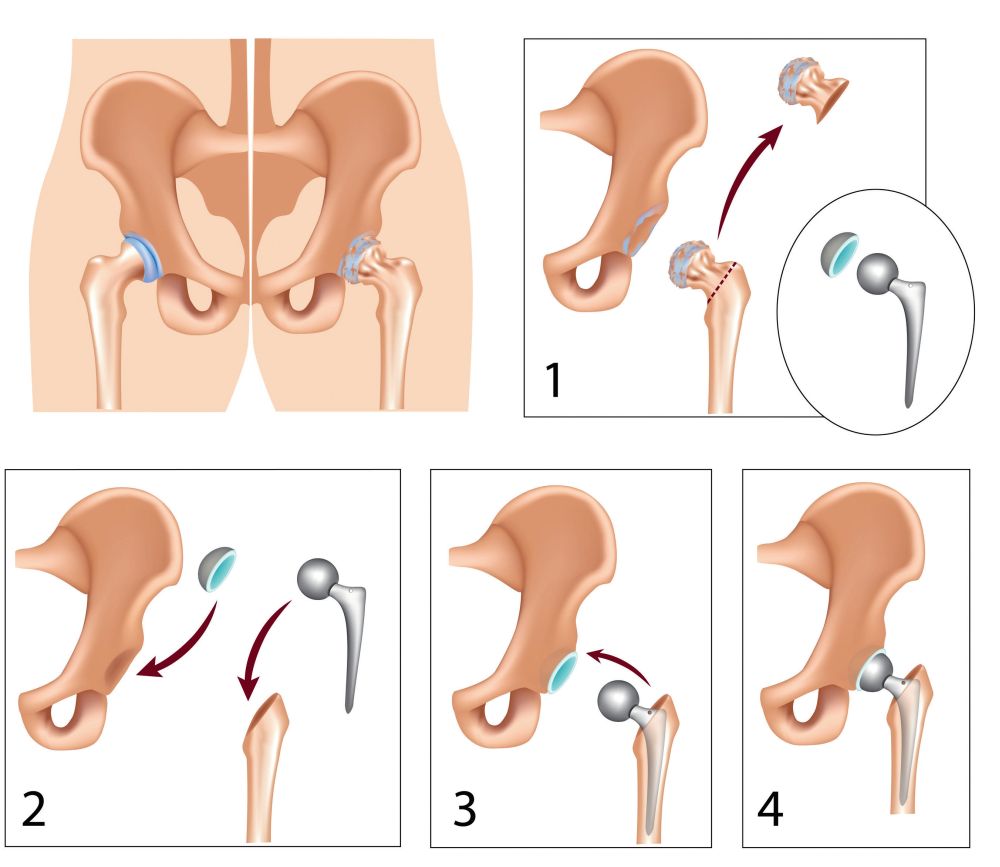
During total hip replacement surgery, the orthopaedic surgeon removes the femoral head after excision of the hip joint (figure 1) and then prepares the bone surface of the articular cavity for the insertion of the articular cavity-part of the prosthesis (plastic component for cemented prosthesis, metal component + plastic insert for non-cemented prosthesis).
After the fixation of the articular cavity part, the surgeon drills the marrow space of the femur for the prosthesis stem (figure 2).
The prosthesis stem is made of metal and can be fixed with or without bone cement. At the end of the procedure, a metal ball is placed on the upper end of the prosthesis stem component (figure 3).
The metal ball fits into the plastic part of the articular cavity component, creating a new, painlessly movable joint (figure 4).
How to prepare for surgery?
Prior to the implantation of the prosthesis, the patient undergoes an examination performed according to strict rules (laboratory and urine tests, nose and throat swab culture, anaesthesiologic examination, if necessary, internal medicine and other consultation deemed necessary by the anaesthesiologist).
With a few exceptions, our patients also have the option of autotransfusion. In this case, one’s own blood is drawn before the operation, so that if anaemia is detected in the postoperative period, the patient will receive the blood they had previously given.
A light dinner is available before surgery, but fluid intake is not allowed from midnight.
Our prosthetic surgeries are performed under antibiotic protection. Only medications dispensed by our nurses can be taken in our ward.

What to do after hip prosthesis implantation?
The day after the operation, the patient can sit on the edge of the bed, stand up, and begin physiotherapy with the involvement of a physiotherapist. Unless otherwise directed by the operating physician, you can put your full weight on the operated limb after surgery.
The length of hospital stay is usually 5 days. Suture collection: 10-14 after surgery.
During the first 3 months after implantation of the prosthesis, certain movements cannot be performed (leaning deep, knee clenching, sitting with crossed legs, etc.). These are brought to the attention of patients by both the operating doctor and the physiotherapist.
Even in the hospital and after being discharged, it is necessary to apply the learned physiotherapy and exercise the limb regularly to the limit of pain, which is essential for recovery.
After a hospital stay, aftercare (rehabilitation) can take place in Visegrád. In the 6 weeks after surgery, we recommend the use of an aid, the use of thrombosis prophylaxis for 30 days, and the wearing of compression tights on the lower extremities. Follow-up examinations are performed at 6 weeks, 3 and 6 months after surgery, and then annually.
What are the benefits of hip replacement surgery?
After surgery, the patient’s hip joint movement is complete again (unobstructed) and painless. After the operation, the patient can live a full, active life again and can even exercise excluding certain types of movements, which are not recommended for hip prosthesis.
What are the risks of the intervention?
Specific risks of hip replacement surgery may include:
- Bruising of the surgical site
- The need for blood transfusion in case of blood loss
- Infections
- Impaired locomotor function due to scarring of the joint capsule
- Limb length difference, which is mostly minor and can be easily tolerated
- Fracture (very rare), wear (normal life 10-15 years), or loosening of the prosthesis
- Fracture of the femur or pelvic bone when the prosthesis is implanted, it may require additional screwing and plating
- Calcific adjacent muscles can lead to postoperative pain and narrowing of the range of motion
- Sprain of the hip prosthesis, which requires repositioning during anaesthesia
- Metal sensitivity or metal allergy, which is very rare, it can lead to chronic inflammation or the loosening of the prothesis
Am I fit for hip prosthesis implantation?
In each case, your doctor will decide, based on the preliminary tests, what risk your prothesis will have. An anaesthesiologist is also consulted to determine the risk more accurately. The results of the tests and consultation with the anaesthesiologist are crucial.
What is included in the price of our surgeries?
- costs of the surgery
- costs of anesthesia (local or general anesthesia, postoperative pain relief)
- the costs of the planned hospital stay and care
- necessary medicines and certain medical aids during the stay
- inpatient physiotherapy treatment (if necessary for rehabilitation)
- if necessary, the fee for the planned histological examination
- the price of the first follow-up examination
What additional costs might be expected?
- implants
- consultation with the anesthesiologist (must be done in Medicover)
- pre-operative examinations (if performed by us)
- in case of blood group antibody positivity, the blood matching fee
- hotel service fee for extra care days
- aids for further rehabilitation
- accompanying person staying in the hospital
- day (with one meal) 20 000 HUF
- night (full board) 60 000 HUF
- furthermore, if necessary, the cost of the 2nd follow-up examination is the fee of the specialist examination -50%, the cost of the 3rd follow-up examination is the fee of the specialist examination -30%
The course of the surgery
Before surgery
- pre-surgery specialist consultation, where the specific surgical proposal is made
- consultation with the Case Manager
- general information if necessary
- preparation of a written quotation
- booking surgery and preliminary examination appointments
- payment
-
carrying out pre-operative examinations
-
arrival for surgery
On the day of surgery
- arrival at Medicover Hospital at 6:30
- check-in at the reception on the ground floor
- occupying a room accompanied by a nurse, who provides information
- morning visit with the specialist physician and anesthesiologist
- surgery
- postoperative monitoring
- afternoon visit with the specialist physician
- constant anesthesiology specialist monitoring in the postoperative period
- discharge (with an accompanying person), final report and handing over a certificate
Surgical service process
- surgery
- hospital stay and care
- planned histology
- follow-up examination, sutur removal
