Fallopian tube patency test (HyCoSy)
There are several methods available to today’s medicine to determine the cause of infertility. The use of each diagnostic method depends mostly on the patient’s medical history.
Infertility of organic origin
The mapping of pelvic anatomical conditions is suitable for the exclusion of organic infertility:
- the cavity of the uterus,
- the patency of the two fallopian tubes,
- the environment of the fallopian tubes to rule out possible adhesions.

Organic infertility is often caused by an inflammatory disease:
- appendicitis
- fallopian tube inflammation
- sexually transmitted diseases
- complicated abortion
We must also consider non-inflammatory factors:
- benign tumour of the uterus, myomas
- pelvic adhesions due to endometriosis
When is it necessary to have a fallopian tube patency test performed?
Fallopian tube patency testing is usually performed for three reasons:
- when examining infertility of unknown origin (when there was no spontaneous pregnancy after one year, with sexual intercourse and without protection)
- before fertilization treatments
- to clarify abnormalities detected during ultrasound examination
It is important to note that infertility (andrological) examination of the male partner is absolutely necessary before the procedure.
The fallopian tube patency test works on the principle of delivering a contrast agent through the cervix into the uterine cavity and checking the patency of the fallopian tube by vaginal ultrasound.

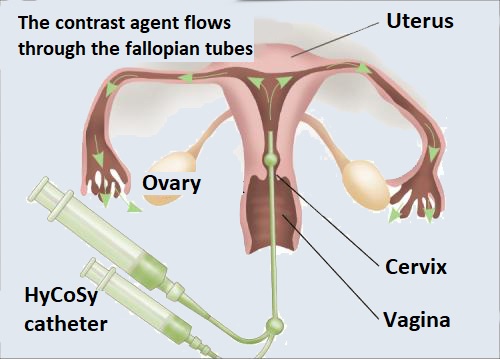
How is the HyCoSy examination performed?
Ultrasound HyCoSy (Hystero-contrast-sonography) is used to examine the uterine cavity and fallopian tube patency relatively quickly and easily in an outpatient procedure with minimal pain.
During the examination, sterile physiological saline is delivered through the vagina into the uterine cavity using a catheter, and then the pressure and rate at which fluid can flow through the fallopian tubes into the abdominal cavity is monitored. If the results are favourable, at least one of the fallopian tubes is sure to be patent.
If the injected fluid is not drained from the uterine cavity into the peritoneal area after a prolonged, high-pressure attempt of 1-3 minutes, both fallopian tubes can be assumed to be blocked. Later consultations are aided by the pictures taken during the examination.
The total duration of the examination is about 1 hour, which includes the preliminary data reconciliation and basic gynaecological examination, the intervention and the imaging procedures, as well as the evaluation of the findings following the examination and the consultation of further questions and possibilities.
How do I prepare for the HyCoSy examination?
The fallopian tube patency test with the HyCoSy procedure is considered an invasive procedure and therefore requires safety preparations. The procedure is scheduled for the time immediately after the menstruation cycle.
It is not advised to eat solid food for 6 hours before the examination, only fluid intake is recommended.
What are the advantages of the fallopian tube patency test?
- can be done on an outpatient basis
- the test is quick
- it is less painful
- free of x-ray exposure
- it does not need to be performed under anaesthesia
What are the disadvantages?
- in the case of active pelvic inflammatory disease, the test is not applicable
- assumes high pressure
- does not provide information on pelvic conditions
What should I expect after the examination?
10-30 minutes after the examination, our patients leave without complaints and in generally good condition, yet we recommend that you arrive with a companion and do not drive a car that day.
In case of complaint, analgesics can be used.
Because we perform a uterine surgery, which is considered a minor gynaecological operation, checking your temperature daily is required for a week afterwards, as well as avoiding a sitting bath and sexual intercourse.
What are the risks of the intervention?
Complications such as pain, nausea, possibility of vomiting, or a drop in blood pressure may occur during the fallopian tube patency test. However, these symptoms are extremely rare due to adequate drug protection.
Subsequent complications may include a few days of discomfort due to peritoneal irritation and possibly peritonitis, which can be eliminated with treatment.
