Laboratory testing of inflammatory bowel diseases (ASCA IgA/IgG)
The ASCA IgA/IgG laboratory test is used to examine the immunological involvement of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and to diagnose Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
What is inflammatory bowel disease?
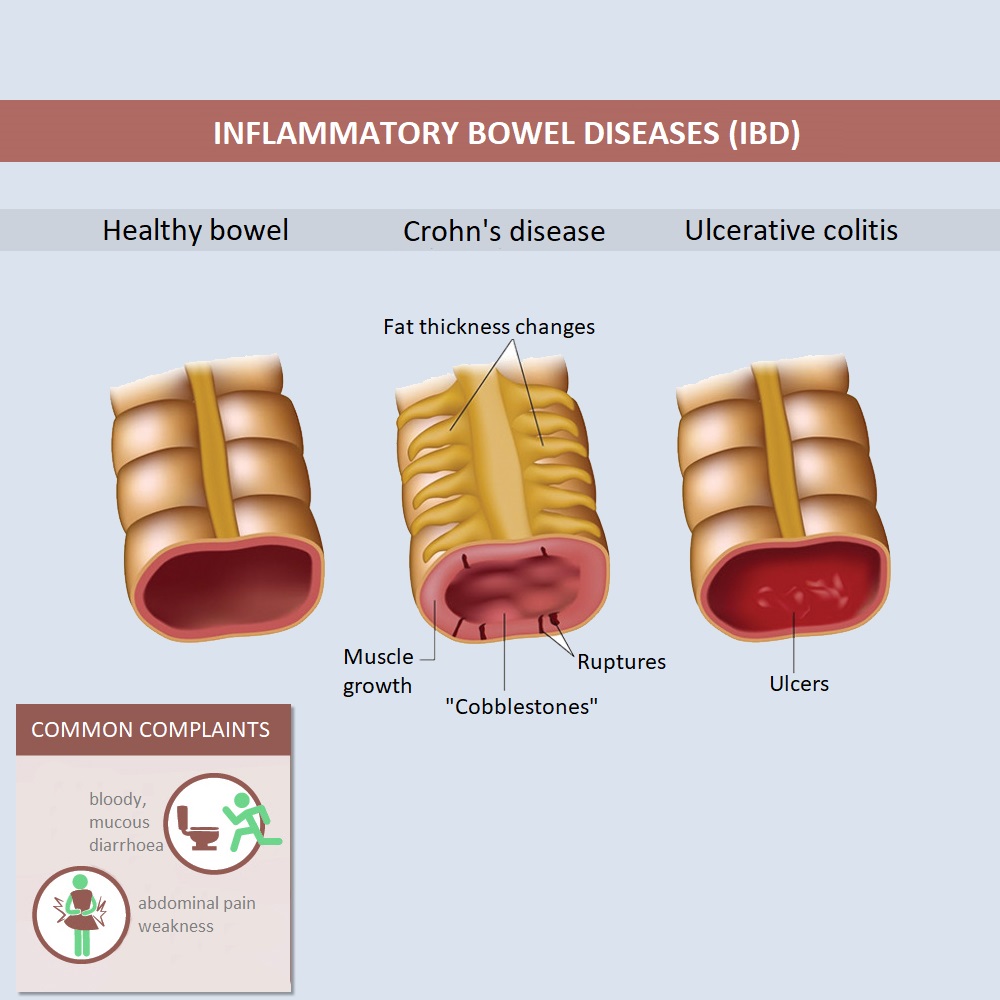
Inflammatory bowel disease, also known as IBD, is a condition associated with chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract. It covers two different conditions, which, however, show similarities in their symptoms and course: Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
In case of both diseases, inflammatory processes appear following the immune response of the immune system, which leads to the development of symptoms. This immune response is accompanied by the destruction of intestinal cells.
The characteristic symptoms are the same in the two diseases: abdominal pain, bloody, mucous diarrhoea, bloating, malaise, fever, fatigue. Moreover, both diseases have characteristic, disease-specific symptoms. Complaints occur intermittently in both diseases, with symptomatic and asymptomatic periods.
The development of the disease requires a complex interaction of several factors: genetic predisposition, environmental factors (stress, diet, medications, sleep), imbalance of the intestinal flora.
In Hungary, nearly 40-50 thousand people are affected by some form of inflammatory bowel diseases. They can develop at any age, but their occurrence is most common between the ages of 15 and 30 years. What they have in common is that they last a lifetime, but they can be treated well, with the help of which the patient can be asymptomatic.
What do you need to know about Crohn's disease?
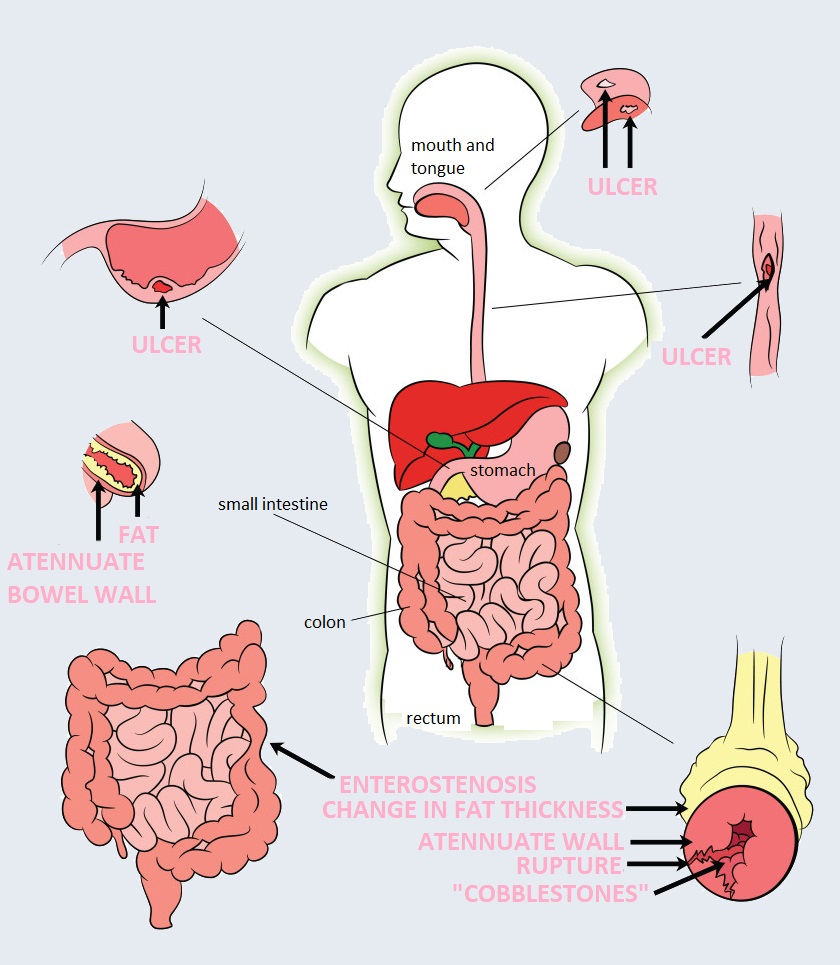
Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel diseases, a chronic gastrointestinal disease. The immune response given by the patient’s body damages the intestinal mucosa, resulting in inflammation of several sections. It most often affects the last section of the small intestine as well as the first section of the colon, but can develop in any part of the gastrointestinal tract. It mostly occurs not in a coherent way but in spots.
As a result of the disease, surface lesions occur at first, and then ulcers on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract. Since the disease affects not only the superficial mucosa but also deeper layers, these ulcers can deepen and converge, causing a number of complications. In severe cases, intestinal perforation may also develop.
In addition to the general symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease (diarrhoea, abdominal pain, nausea, fatigue, fever), Crohn’s disease is characterized by weight loss and vitamin deficiency, as well as malnutrition. In addition to gastrointestinal complaints, other symptoms such as joint complaints, gallstones, kidney stones, urinary tract infections, eye and skin symptoms may occur.
The course of the disease varies from individual to individual, and the length of the symptomatic and asymptomatic periods may vary.
What is ulcerative colitis?
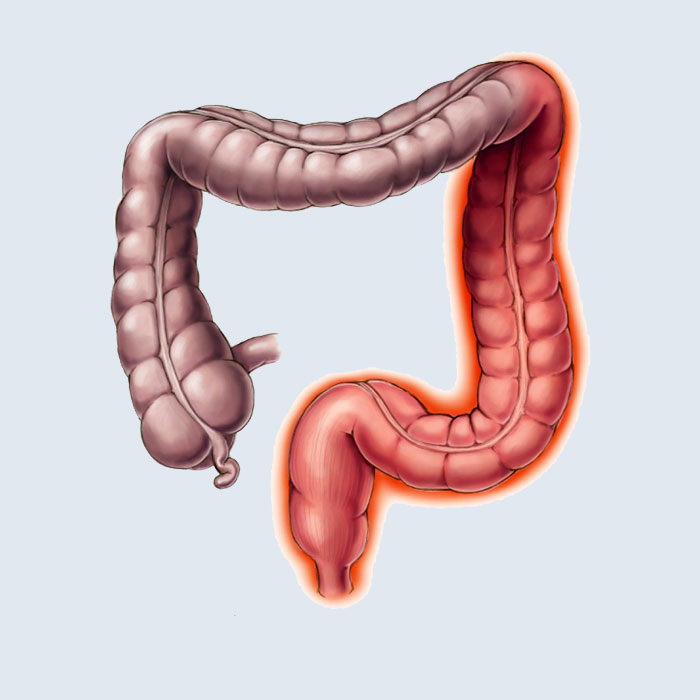
Ulcerative colitis is another type of inflammatory bowel disease. The disease results in abrasions on the colonic mucosa and, in more severe cases, ulcers. The disease usually develops first in the rectum and spreads upwards to a certain point, causing a contiguous inflammation in the affected area. Inflammation lasts up to the transition from the small intestine to the colon.
In case of this disease, the mucous membrane of the colon is affected, the protective function of the mucosa is reduced, so intestinal bacteria can enter the intestinal wall. They activate the immune system, which results in a complex defence reaction, inflammation.
In addition to the general symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease, the characteristic symptom of ulcerative colitis is the urge to defecate. Non-digestive symptoms such as joint pain, skin symptoms and, in some cases, eye inflammation may also occur.
Ulcerative colitis also alternates between symptomatic and asymptomatic periods. The disease can flare up for no reason, but stress is a major risk factor. With the help of medication, periods of flare-up can be kept under control and made complaint-free.
What is the ASCA IgA/IgG test good for?
Using the ASCA IgA/IgG laboratory test, autoantibodies characteristic of inflammatory bowel disease can be detected in a blood sample at an early stage, in a non-invasive way (without intervention).
What exactly are we examining?
ASCA (anti-saccharomyces cerevisiae) is an autoantibody against “baker’s yeast” (fermentum officinae cerevisiariae) that is produced against manna in the wall of yeast. The test shows that this autoantibody can be detected in the blood of some patients in the early stages of the disease in case of Crohn’s disease, suggesting the presence of Crohn’s disease.
To differentiate, to determine if Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis is causing the complaints, it is recommended that an ANCA test be performed concurrently, the positivity of which indicates ulcerative colitis.
How do I prepare for the test?
No preparation is required for the test.
How is sampling done?
Sampling is done through a sampling needle inserted into a vein.
When is the result expected?
Within 9 working days after the examination.