Laboratory testing of female menopause hormones
We recommend the tests of this package at the beginning of menopause, in case of menstrual bleeding disorders, heatwaves, and rapid pulse. The tests in the package look at changes in hormone levels that can be linked to menopause.
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
It is a protein that is produced by the pituitary gland, not the thyroid gland, and is needed for the thyroid gland to function properly. If the value of TSH is increased, we talk about hypothyroidism, if the value of TSH is significantly reduced, we can often talk about hyperthyroidism.
What could be behind the low value?
- Due to increased thyroid function (hyperthyroidism), high T4 and T3 levels inhibit the pituitary TSH production, resulting in low TSH levels.
- In case of thyroidectomy or known hyperthyroidism, overdose of drug therapy and high doses of hormone preparations also reduce the value of TSH in the blood.
- In rare cases, TSH is not produced due to damage to the pituitary gland.
- Decreased TSH levels can also be seen during pregnancy.
What can be behind the high value?
- Elevated TSH levels are most commonly associated with hypothyroidism.
- High TSH levels can be caused by acute or chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland.
- Surgical removal of the thyroid gland (removal involves a decrease or cessation of the production of thyroid hormones).
- During drug treatment of a thyroid patient (thyroid hormone replacement): a lower dose of the drug than necessary.
FSH
FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone, follicular maturation hormone) is a sex hormone produced in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Although FSH and LH are required for normal sexual function in both men and women, the process of excretion in the body is very different for the two sexes.
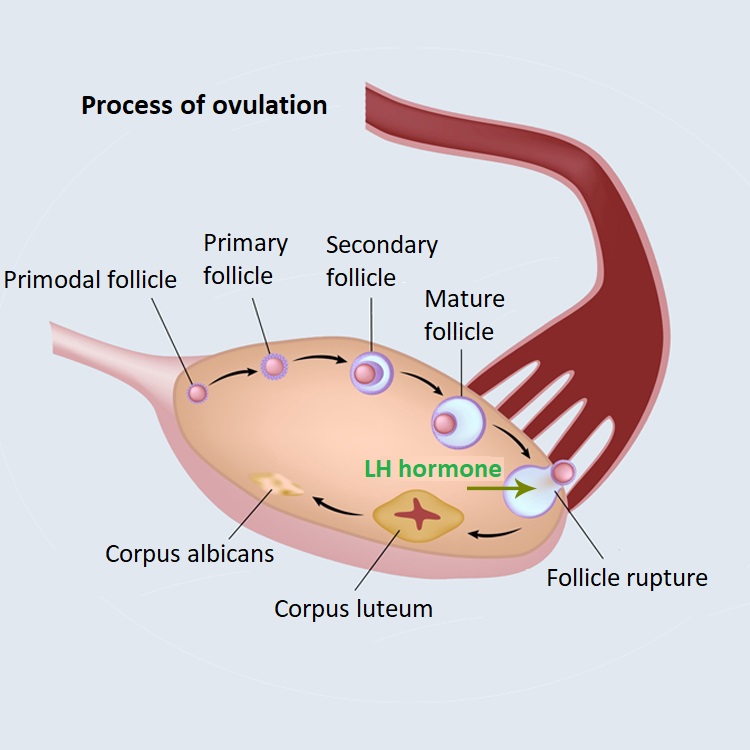
FSH initiates the growth and development of ovarian follicles. During ovulation, the follicle ruptures, the egg is released and the corpus luteum forms. In menopause, decreased ovarian function results in a decrease in oestradiol secretion, resulting in a significant increase in circulating FSH levels.
When may the test be needed?
Diagnosing menstrual disorders, infertility, menopause, pituitary gland and diseases associated with ovarian disorders.
When a woman reaches menopause and her ovaries stop functioning, FSH levels rise.

LH (luteinizing hormone, corpus luteum stimulating hormone)
LH is a sex hormone that is produced in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland (pituitary gland). LH triggers ovulation (follicular rupture, ovulation). It further matures the follicle prepared by FSH; when LH levels increase, ovulation occurs. LH also stimulates the production of steroid hormones (estrogen and progesterone) in the ovaries.
During menopause, when the ovaries stop working, LH levels remain elevated.
For infertile women with reduced fertility and for infertile women treated with gonadotropins, its determination may provide information about the onset of ovulation.
When may the test be needed?
In the diagnosis of menstrual disorders, infertility (infertility), menopause (menopause), pituitary gland and diseases associated with ovarian disorders. When a woman reaches changing age (menopause) and her ovaries stop functioning, LH levels rise.
Other causes of missing follicular rupture may include: polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), adrenal gland disease, thyroid disease, ovarian tumour.
Oestradiol
It is a member of the oestrogen family (estrone, oestradiol, estriol). In women, it is mainly produced in the ovaries and placenta. Adequate levels are needed for egg maturation, conception and pregnancy, as well as maintaining healthy bone mass. Additionally, it is involved in the regulation of cholesterol levels and the development and maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics. Oestradiol levels increase during pregnancy as the placenta also begins to produce it. During menopause, oestradiol production becomes irregular and occasionally paused.
How do I prepare for the test?
If you still have a cycle, even if it is irregular, we recommend you have the blood count between days 2-5 of the cycle. If you do not have a period anymore, any day is suitable for sampling.
Having and empty stomach is not required for the female menopause laboratory test.
When is the result expected?
After the 3rd working day following the test.