Nephrology
The science of renal internal medicine is nephrology, which deals with the functioning and disorders of the kidneys. Urology, on the other hand, includes diseases of the urinary system, the male genitals, and the kidneys (e.g., kidney stones, tumours) that require surgery.
What does a nephrologist examine?
The nephrologist examines the functional abnormalities of the kidney (selective function).
Anatomy and main functions of the kidneys
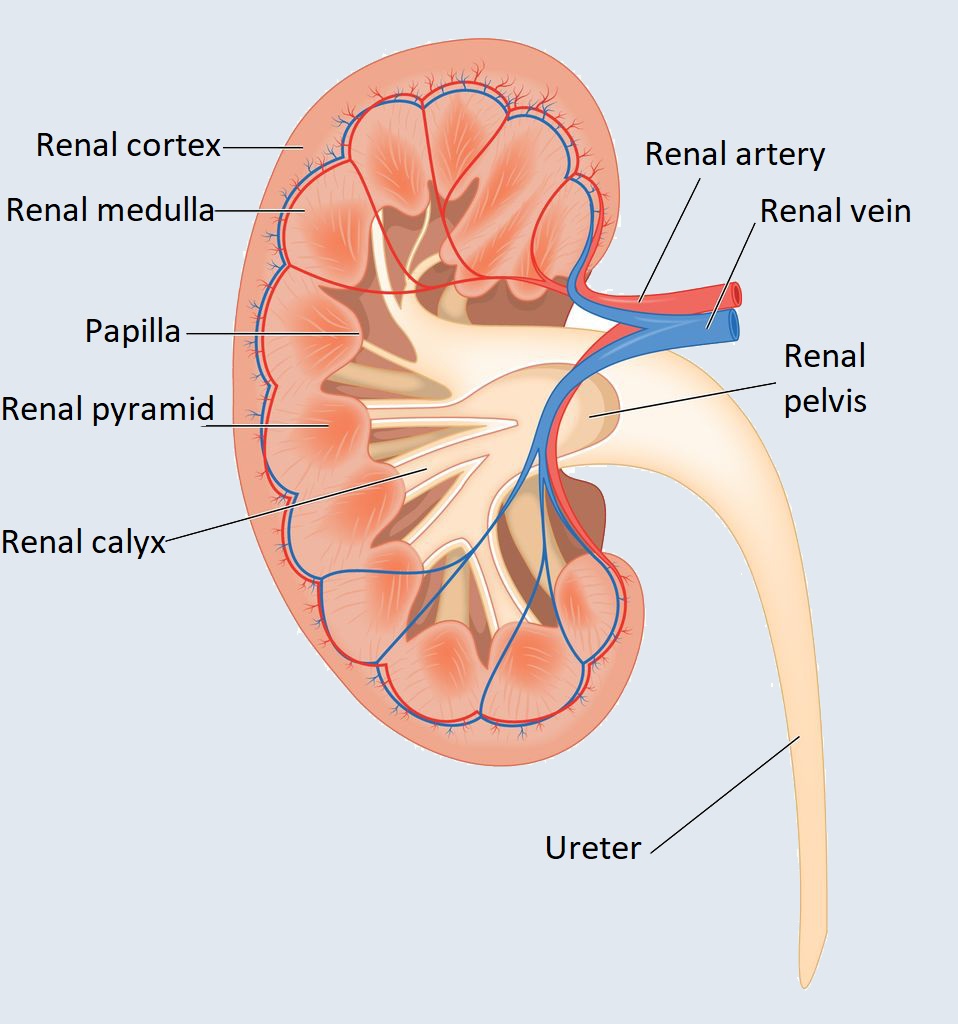
The kidney is a pair of bean-shaped organs located at the back, at about waist height, on either side of the spine. They measure 12 cm x 4 cm and weigh approx. 140 grams.
The kidneys of a healthy adult are smooth and bright brown in colour. It is surrounded on the outside by a three-layer connective tissue case. Below the outer cortex is the medulla. The filtered urine enters the renal pelvis from the collecting ducts and is then excreted from the body through the ureter, bladder, and urethra.
The kidney, according to its main functions, cleanses the blood, starts the production of red blood cells, selects the breakdown products, discharges toxins, produces hormones, and ensures the balance of fluid and mineral household.
Typical symptoms of kidney diseases
Chronic kidney disease is often only indicated by abnormal results from urine and blood tests, as they do not initially cause complaints or produce any noticeable symptoms. In acute or advanced conditions, anaemia, weakness, nausea, too much or too little urine, or shortness of breath and high blood pressure may occur.
When to see a nephrologist?
It is recommended to visit a nephrologist in the following cases:
- acute kidney failure
- chronic kidney failure
- blood urination
- elevated serum urea or creatinine levels
- in case of diabetes if protein depletion or deterioration of renal function occur
- in case of detection of the cause or complication of high blood pressure, especially in the presence of impaired renal function
- urinary tract infections or recurrent urinary tract infections
- for the investigation and treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease
- inherited kidney disease (e.g. polycystic kidney disease)
- in diseases of immunological origin where the kidney is involved
How can kidney function be tested?
The general urine test gives information about the composition of the urine, while blood test about the urea, creatinine and carbamide values. Ultrasound examination of the kidneys clearly shows the shape, size, glandular substance, renal vessels and the renal cavity system (renal pelvis, ureter).
