Plastic surgery
As part of plastic surgery, we remove skin lesions such as fibroids, lipomas, basal cell carcinomas, atheroma, moles, and surgical scars.
The removal of skin lesions on our body with the help of a plastic surgeon can be done for aesthetic but also health reasons, depending on the type and nature of the lesion. A skin lesion is an abnormal appearance of a certain part of the skin, which can be a fatty tumour, a lump of fat, atheroma (a benign tumour under the skin), a fibroid tumour (a benign tumour of the skin), a skin growth, a mole, a wart or a surgical scar.

What happens during outpatient plastic surgery?
Our plastic surgeons remove skin lesions with surgical excision under local anaesthesia after disinfecting the area to be treated. Depending on the nature and extent of the skin lesion, the operation lasts 15-45 minutes. Following excision, the removed tissue should be subjected to histological examination if necessary.
During surgery, the plastic surgeon makes the smallest incision possible. The wound edges are contracted with a special welt thread called plastic stitching. This creates a barely noticeable, thin scar. Finally, a sterile bandage is applied to the wound.
The surgery is done on an outpatient basis. The patient may return home immediately after treatment. Wound examination takes place after one week and suture removal after two weeks.
Surgical procedures
Within the framework of plastic surgery, the following interventions are performed:
- Removal of fibroids
- Removal of lipomas
- Removal of basal cell carcinoma
- Removal of atheroma
- Birthmark removal
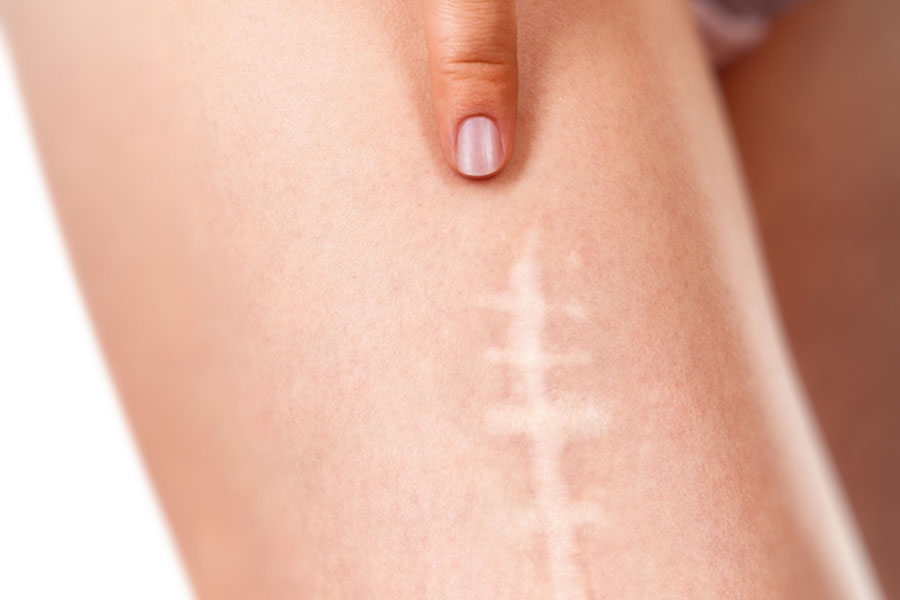
- Scar plastic surgery
What do you need to know about skin changes?
Fibroma
Fibroma is a soft, brownish lesion that can appear on any part of the body. Benign cell proliferation of connective tissue cells. It usually does not cause a complaint, but aesthetically it can be annoying. In terms of its types, we distinguish between hard fibroids (low in cells), soft fibroids, also known as “proud flesh”, keloids (proliferation of scars due to injury or injuries), angiofibroma (dilated blood vessels between connective tissue cells) and cystic fibrosis (there are lymphatics between the connective tissues).
Lipoma
Lipoma (a lump of fat) is a benign skin tumour. The connective tissue lesion is well separated from the surrounding tissues. It is growing slowly. It mostly develops in the subcutaneous adipose tissue on the torso, legs or arms. The more connective tissue a lipoma contains, the harder it becomes. It causes the mostly aesthetic problems.
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a malignant skin tumour that grows slowly. It develops from stem cells in the lower cell layer of the epidermis. It rarely causes metastasis. In most cases, the tumour develops on the surfaces of the skin (face, ears, chest, back) that are permanently exposed to sunlight (UV-B rays). However, in some cases, it can also develop on skin areas that are protected from sunlight.
Atheroma
Atheroma is a benign tumour located under the skin. It consists of a connective tissue sheath and the contents produced by it in the sebaceous gland. It got its name because of the porridge-like sebum produced by the glands. A hose filled with sebaceous gland secretions is formed when the outlet of the gland is blocked for some reason, so the sebum produced in it accumulates, resulting in swelling of the gland.
Birthmark
A mole is a sharp-boundary lesion on the skin that is formed at birth or later, its colour and surface is different from your skin. It is usually a few millimetres big but can grow larger than that. Its colour is dark, yellowish brown, sometimes black. Its surface may be smooth or uneven, its shape may be circular or irregular. In the case of later-formed moles, new ones may be formed because of UV radiation, during adolescence and pregnancy. Excision of a given mole is justified if it causes an aesthetic problem, can easily get caught in anything in terms of location and surface, or if a cancerous lesion (melanoma) is suspected.
Scars
Wounds caused by minor accidental injuries or surgery, heal with a scar. These scars can be aesthetically annoying in some cases, as scar formation is affected by a number of factors (skin type, age, genetics, allergic reaction, infection, irritation, pregnancy, etc.).

