Paediatric nasal tonsil surgery (Adenotomy)
During nasal tonsil surgery (adenotomy), an enlarged nasal tonsil located on the back wall of the nasopharynx is removed.
In our hospital, it is possible to perform pediatric tonsil surgery over the age of 3.
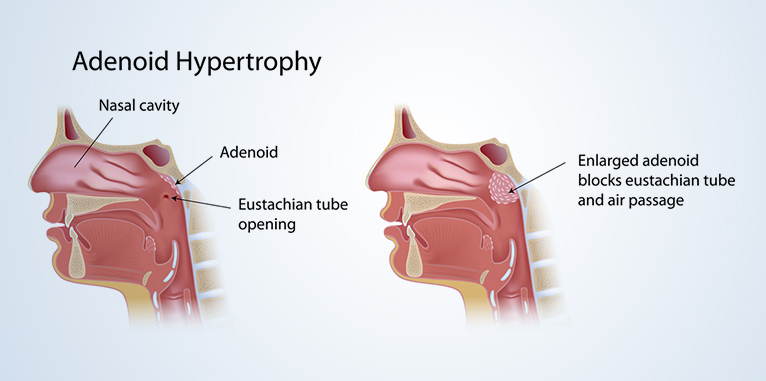
The nasal tonsil is a spongy organ in the upper part of the pharynx, in the nasopharynx. Due to its location, it is also referred to as throat almonds. It is part of the lymphatic system, as part of a ring of lymphoid tissue (Waldeyer’s ring), which is an important factor in local defense against infections, the body’s first immunological screening station, especially in infancy and childhood.
Its size is about the size of a fingertip, which is normally covered by the palate. Only the significantly enlarged nasal tonsil becomes visible, which can hang into the pharynx. Children’s tonsils contain white blood cells that produce antibodies.
These antibodies play an important role in protecting against nasal and oral bacteria. As the age progresses, the nasal tonsil shrinks or disappears, so it does not play an additional protective role. If the tonsil is chronically infected, swollen, and inflamed, it can cause breathing difficulties, which occur primarily during sleep.
In what cases is nasal tonsil surgery recommended?
Nasal tonsil surgery is recommended if the enlarged nasal tonsil inhibits nasal breathing, causes chronic ear pain, ear inflammation, or hearing loss. If its size reaches a size that causes symptoms or chronic inflammation develops, removal is the only option from which a lasting result, healing, is expected.
A common cause of chronic otitis media is an abnormally enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil, which can block the openings in the eardrum. As a result, the drum cavity cannot be properly ventilated and accumulating whey results in permanent inflammation.
When the enlarged nasal tonsil closes the nasopharynx, nasal breathing difficulty, closed nasal speech, is observed. Nasal discharge due to occlusion can cause and maintain stagnant acute / chronic sinusitis. Leaking discharge from a chronically infected nasopharyngeal tonsil can lead to cough, laryngitis, and bronchitis, exacerbate any asthma symptoms that may exist, or cause them to recur. Thus, removal of the tonsil is absolutely warranted in case of recurrent and / or chronic otitis media, persistent hearing loss, dyspnea, chronic sinusitis and bronchitis.
What are the risks of not having surgery?
- The risks of not having surgery can always be determined with an accurate knowledge of the case, but in general it can be said an absolutely justified surgery failure to have surgery can have serious consequences.
- Chronic nocturnal respiratory complaints due to nasal congestion can provoke cardiovascular and nervous system diseases.
- A child with tonsillectomy is often inattentive and insomnia, and his mouth is often open during the day, which can make his facial expression typically “dull”.
- In the absence of nasal tonsil surgery, nasal tonsil hypertrophy is a permanent, in many cases only surgically correctable hearing loss, chronic inflammation of the upper respiratory tract and paranasal sinuses, exacerbation or exacerbation of bronchial asthma and chronic bronchitis, sleep apnea.
How does the surgery go?
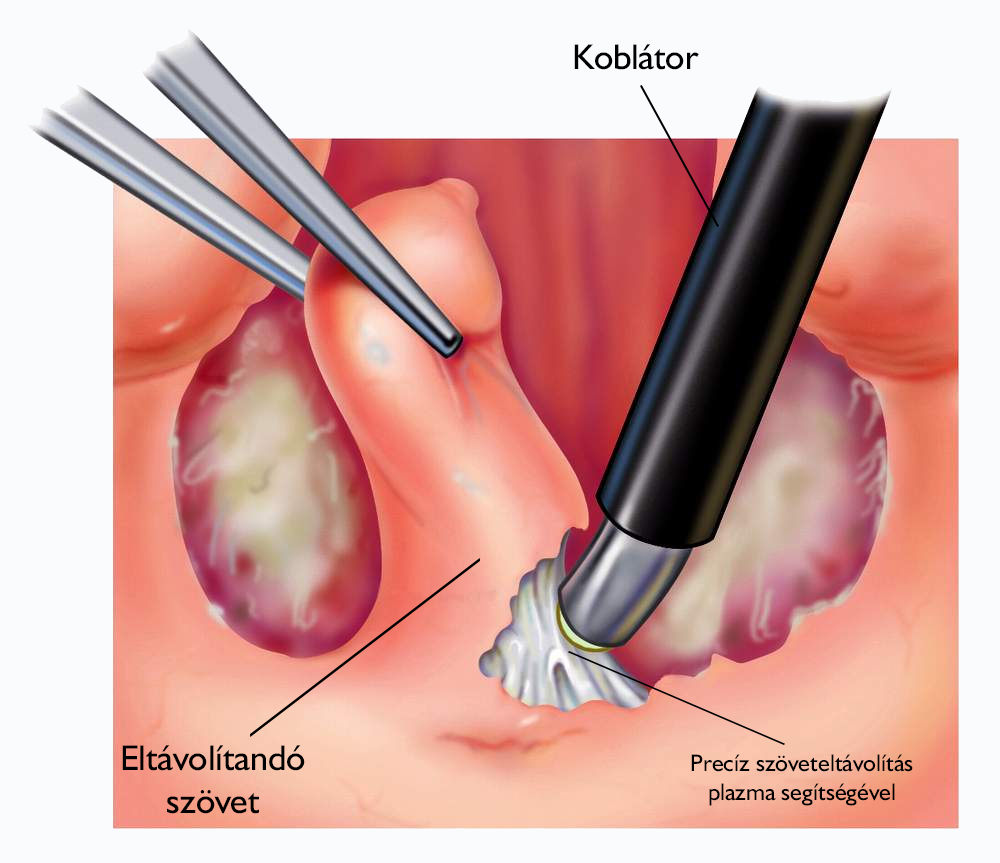
The child’s tonsillectomy is performed under general anesthesia in all cases. The nasal tonsil is removed orally with a device called an adenotome by a conventional excision or coblation procedure.
An otolaryngologist performing surgery during a conventional excision removes the tonsil from the back wall of the pharynx, making sure that as little lymph tissue as possible remains.
One of the biggest advantages of the coblation, also known as cold plasma cutting procedure, in addition to faster wound healing, is also much milder wound pain after surgery. The essence of the method is to create a focused plasma with the electrically excited electrolyte (NaCl), which breaks down the tissue molecular bonds at low temperatures, the cutting is practically done by evaporating the tissues. As a result, a uniform, fine anatomical surface is formed at the site of the incision, where the wound does not require suturing either, because the plasma incision occludes the small blood vessels at the same time, so that no bleeding occurs. This significantly shortens the recovery time after surgery and results in less pain and discomfort after surgery as no sutures are required either.
During tonsillectomy, a hemostatic swab is used to control the bleeding during surgery. If this does not control the bleeding, electrical hemostasis, possibly a nasopharyngeal swab for 1-2 days is required. Nasal tonsil removal can be performed at the same time as sore tonsil surgery.
How to prepare the child for surgery?
For the child, the hospital is a completely new environment, so the first consultation is already a lot of excitement. For this reason, it is important to prepare what awaits him here.
According to his age, we tell him that he has to go to get rid of the complaints he has visited his uncle / doctor many times before, and tell us in detail what and how it will happen, who he will meet in the few days he has to spend in the hospital . It is important to make him aware that this is all done for his healing.
As parents ’peace of mind and serenity can be the greatest help in this, our specialists and case managers provide the most detailed information possible about the procedure prior to surgery, and answer any questions that may arise during consultations. During the recovery period, our hospital staff will also be happy to help make these few days even more comfortable for both the child and the parents.
We believe that parental presence is the greatest healing force for small patients and at the same time the most reassuring for parents, so we provide one parent with the opportunity to stay during their stay in the hospital.
What are the risks of tonsillectomy?
As with any surgical procedure, there are general risks and dangers to pediatric tonsillectomy, about which the surgeon will provide detailed information prior to surgery.
After surgery, mild or more severe nosebleeds, bloody sputum, bloody vomiting, cough stimuli, cough, and severe restlessness may occur in the patient on the day of surgery. The child may be weak, drowsy and dizzy due to the varying amount of blood loss, surgical stress and medications used, and fever, headache and nausea may occur. After nasal tonsil surgery, blood clots in the nose and swelling of the nasal mucosa may cause spasmodic, blocked nasal breathing.
What to do after removing the tonsil?
- Complete bed rest is required on the day of tonsillectomy. Following surgery, the little patient must spend one night in our hospital under observation. For the duration of the recovery period spent in our hospital, we provide one parent with the opportunity for continuous stay so that the days spent in the hospital can be spent in complete peace for both the child and the parent.
- 3-4 hours after the operation, you can consume fluids and pasty foods, then in the following days a dietary, pasty diet is recommended, with an abundant (1-1.5 liters) fluid intake.
- After nasal tonsil surgery, blood clots in the nose and swelling of the nasal mucosa may cause spasmodic, blocked nasal breathing. In many cases, the nasal, nasal speech voice changes, in children the voice may become slightly higher.
- Do not blow your nose for 2 weeks after surgery, only wipe if necessary. In all cases, try to reassure the child not to cry.
- Following nasal tonsil surgery, there is usually no pain other than a mild throat scraping that lasts for 1-2 days.
- Due to the risk of bleeding, physical sparing is extremely important for 2 weeks: jumping, squatting and heavy lifting are prohibited. Anything that causes head blood clots (hot bath, washing hair with warm water) should be avoided.
- If significant bleeding occurs, report it immediately to our Hospital or on call at the specified otolaryngology to relieve the bleeding as soon as possible.
- If you have any other complaints in the days after the operation, feel free to contact our colleagues.
- It is important to know that the tonsils can grow back years after removal.

How long is the recovery?
Wound healing after nasal tonsil surgery is completed 7-10 days after leaving the hospital.
During this period, the child needs care and parental supervision, as there is a high risk of postoperative bleeding in the surgical area.
If a child has no complaints, he or she can go to school, kindergarten or nursery after about a week and a half, but it is recommended that he or she be exempted from physical education for another three weeks.
Convenience services
We accommodate our clients in a modern, pleasant, air-conditioned single room. Each room has a private bathroom, fridge and TV, and free WIFI access. We also provide our clients with individual nurse supervision, who will help your continuous recovery during your stay.
